
Splunk
スプランク
Splunk O11y Cloud ブログ ~ No samplingの強み ~

目次
はじめに
近年の大規模なアプリケーション開発では、変化に応じた素早く継続的な開発が必要となり、アプリケーションを小さなマイクロサービスの集合として構築するマイクロサービスアーキテクチャへの移行が進んでいます。このようなアプリケーション開発の流れから、オブザーバビリティ(Observability, O11y)、つまり数十~数百のマイクロサービスを俯瞰的に監視し、障害発生時には根本原因特定のために、ユーザーが閲覧するフロントエンドからインフラストラクチャーまでを一気通貫に状態確認できる仕組みが必要となっています。
高いオブザーバビリティの状態実現のためには、フロントエンド、バックエンド、インフラストラクチャーの大量のログ、メトリクス、分散トレース等のデータをアプリケーションから取得し、可視化する必要があります。しかしながら、データ保存・加工ツールのスペック制限の観点からすべてのデータを使用することは難しく、データはサンプリングされ、一部のデータからオブザーバビリティをかたちづくるツールがほとんどです。
※分散トレース:
ユーザーからのリクエストに伴う様々なサービス呼び出しやデータストアへのアクセスなど、一連の処理(トランザクション)を追跡・管理できるようにパラーメータ等を組み合わせたログ。
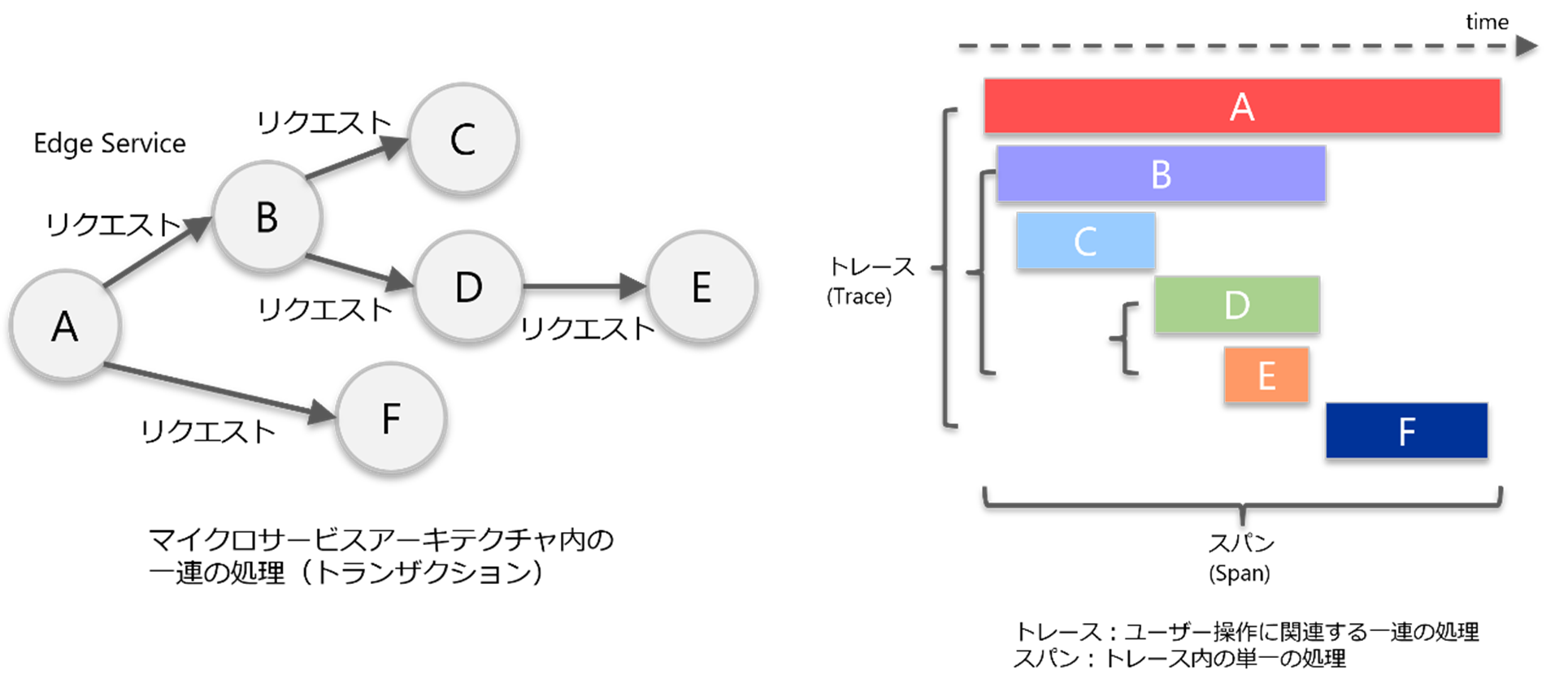
左図:トランザクション例、右図:分散トレース例
サンプリングによるトラブルシューティングの影響
1. 事象発生時の対応の遅れ
同一の根本原因から発生する複数パターンの事象が発生している場合、サンプリングにより一部のパターンしか早急に把握できず、すべての発生パターンの確認に時間を要します。一部のパターンからの類推では根本原因にたどり着くスピードが遅くなります。
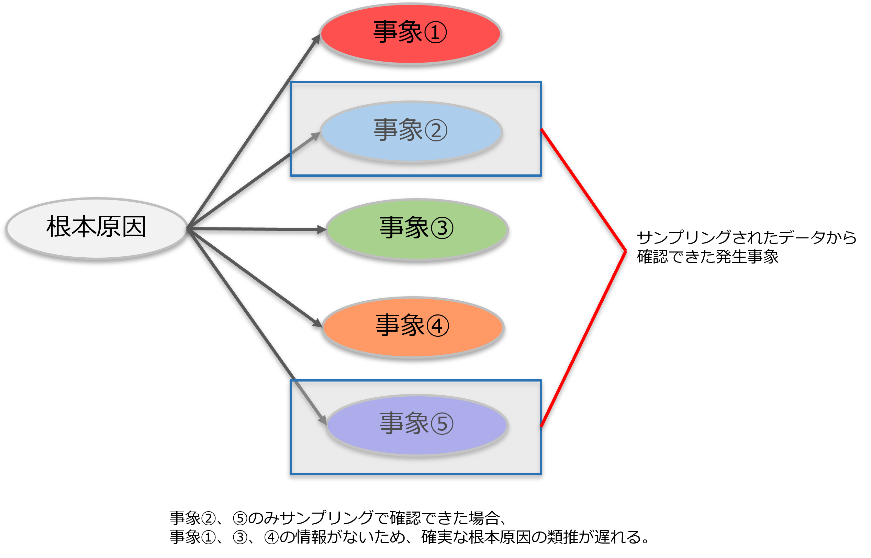
事象発生時の対応の遅れ
2. 偶発的な異常の見落とし
偶発的な異常が発生し、サンプリングの間隔で捉えられなかった場合、再度異常が発生し確認するまでの時間が生じます。偶発的な異常がビジネスに重大な障害を引き起こす恐れがあり、異常の確認、対応が遅れることによって機会損失や信頼性低下のリスクに繋がります。
偶発的な異常の見落とし
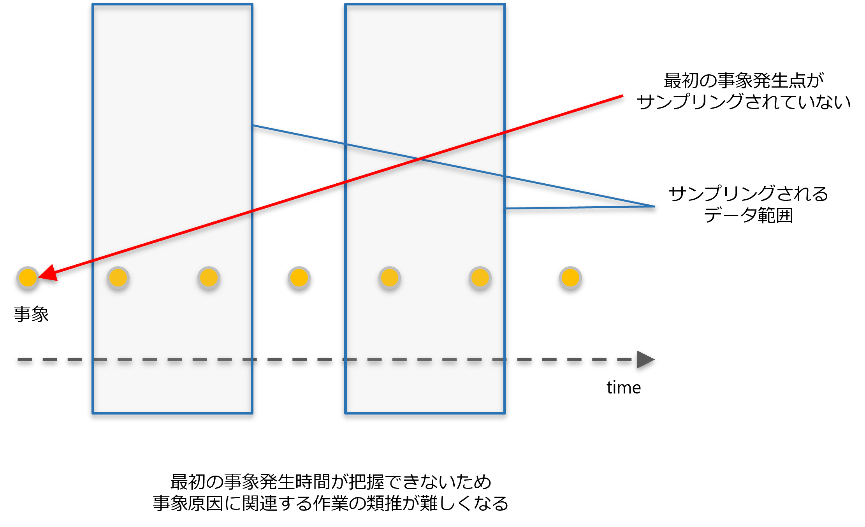
3. 異常発生時点の把握ができない
事象の発生時点をサンプリングで捉えられなかった場合、発生時間が確認できずシステム変更等の作業の文脈から根本原因の類推が難しくなります。根本原因の確認が遅れ、対応スピードが遅くなります。
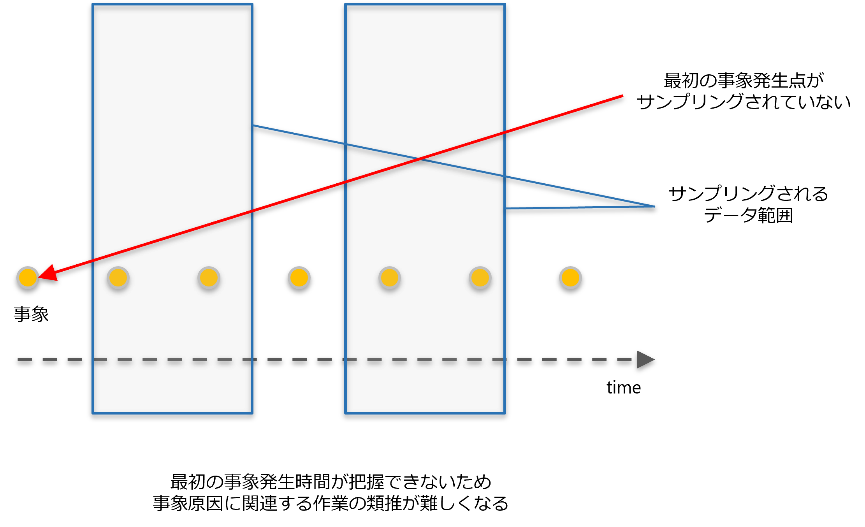
異常発生時点の把握ができない
Splunk O11y CloudではNo sampling
Splunk O11y Cloudはすべてのログ・メトリクス・分散トレースに対してサンプリングを一切行わずにデータ取り込みを行っております。データセットの偏りや異常の見逃しがなく、事象発生地点から現在までのすべての事象を把握でき、従来のO11y製品、APM製品と比較して効率的な監視・根本原因の特定が可能になります。
No sampling + リアルタイム性による迅速なトラブルシューティング
Splunk O11y Cloudのリアルタイム・ストリーミング・アーキテクチャによって、1秒間に数万件のトランザクションデータをストリーミング処理が可能になり、"分"ではなく"秒"単位で取り込んだデータの解析・可視化が行われます。サンプリングなしのデータ解析とこのストリーミング処理によって、リアルタイムですべての事象を把握でき、すばやく原因特定が可能になります。
おわりに
Splunk社のメッセージにもあるように、サンプリングはオブザーバビリティとは矛盾するアプローチです。一部のトランザクションデータであっても無視することで、システムの状態を完全に可視化することができなくなり、重大なビジネスの問題に発展する可能性がございます。
そのような問題を避け、高いオブザーバビリティを実現するためにもSplunk o11y Cloudのご利用をご検討頂ければ幸いです。
お問い合わせ・資料請求
株式会社マクニカ Splunk 担当
- TEL:045-476-2010
- E-mail:splunk-sales@macnica.co.jp
平日 9:00~17:00




