
Recently, we often hear about "autonomous driving" in TV commercials, but it is expected that the 2020s will be an age of self-autonomous driving cars, where autonomous driving technology will evolve significantly and become widespread in society. Level 3 autonomous driving driving, which enables conditional autonomous driving, and Level 4 autonomous driving, which enables unmanned driving, have begun to be implemented in society.
In order not to miss the age of autonomous driving that has just begun, let's comprehensively explain the basic knowledge related to autonomous driving, such as the mechanism of autonomous driving, the technology that is the element, and the development trends.
level of autonomous driving
In Japan, autonomous driving is divided into six levels, from level 0 to level 5, according to the subject of the driving task and driving area. The standard for classification is the one developed by the US non-profit organization "SAE (Society of Automotive Engineers)", which is the most widely used in the world, and Japan also adopts it.
|
Level |
Name |
Driving subject |
Running area |
|
0 |
No driving automation |
Man |
Not applicable |
|
1 |
Driving assistance |
Man |
Limited |
|
2 |
Partial driving automation |
Man |
Limited |
|
3 |
Conditional driving automation |
system |
Limited |
|
4 |
Advanced driving automation |
system |
Limited |
|
5 |
Full driving automation |
system |
No limited |
Autonomous driving Levels (Reference: JSAE "Summary of Driving Automation Levels")
Levels 1 and 2 are equivalent to ADAS (Advanced Driver Assistance Systems)
Level 0 is 'no driving automation', where the driver performs all dynamic driving tasks. Older cars are at this level.
Level 1 is "driving assistance", in which the system continuously performs either longitudinal or lateral vehicle motion control subtasks of the dynamic driving task in a specific limited area. This is the case with either longitudinal driver assistance systems such as Collision Mitigation Braking or Adaptive Cruise Control, or lateral driver assistance systems such as Lane Keep Assist.
Level 2 is achieved by having both vertical and horizontal orientations. Level 2 is "partial driving automation", in which the system continuously performs both longitudinal and lateral vehicle motion control subtasks of the dynamic driving task in a specific limited area.
When level 2 is advanced, "hands-off" driving, which allows you to take your hands off the steering wheel under certain conditions, becomes possible. Since it is a driving support system, the driver must not neglect to monitor the surroundings of the vehicle, but if such technology evolves further and reaches a technological level that does not require the driver's obligation to monitor, it will be "autonomous driving". .

Level 3, the first step towards autonomous driving
Level 3 is "conditional driving automation", where the system continuously performs all dynamic driving tasks in a limited area. While the system is operating, the driver is able to "eyes off" driving, which exempts them from the obligation to monitor the surroundings of the vehicle, allowing them to relax to some extent inside the vehicle. Sleeping and drinking alcohol are strictly prohibited because you have to carry it.
In Japan, the ban was lifted in April 2020 due to revisions to the Road Traffic Law and the Road Transport Vehicle Law. In addition, international standards were established in June of the same year, and it is expected that the wave of lifting the ban will spread around the world from now on until 2021.
Currently, international standards limit the operation of autonomous driving systems to driving on motorways such as highways at speeds of 60 km/h or less. ODD/operation design area) is also expected to expand.

Level 4 and above can drive without a driver
Level 4 is "advanced driving automation", in which the system continuously performs all dynamic driving tasks and responds to cases where it is difficult to continue operation in a limited area. ODD is set for each autonomous driving system, which is a condition for driving to be possible, and the autonomous driving without a driver is realized. After level 4, it is often called "brain-off" because the driver does not need to think about driving behavior.
Practical demonstrations of level 4 autonomous driving transportation services are being actively conducted in various parts of the world. Most of them operate with a safety driver on board just in case, but in Arizona, Google-affiliated Waymo (Waymo) has started providing de facto Level 4 service without a safety driver from 2019.
Practical demonstrations are also active in China, and it seems likely that operations without safety drivers will start in 2021. In Japan, the goal is to realize an unmanned service with only remote monitoring around 2023-2025.
Level 5 is "complete driving automation", a technology that allows the system to automatically drive under all conditions, such as driving area, speed, and weather. There are many movements aiming for realization in the 2030s, but the hurdles are extremely high, so the timing of realization is currently unclear.

How autonomous driving works
autonomous driving is achieved when the system replaces the driver's abilities related to recognition, prediction, judgment, and operation (control).
Sensors such as cameras, LiDAR (lidar), and millimeter-wave radar installed in vehicles play the role of "eyes", constantly monitoring the surroundings and front of the vehicle, and using image data acquired by the sensors to detect other vehicles and pedestrians. , AI (artificial intelligence) acts as the "brain" to recognize white lines, signs, etc. on the road and determine control such as accelerator, brake, and steering wheel to drive safely.
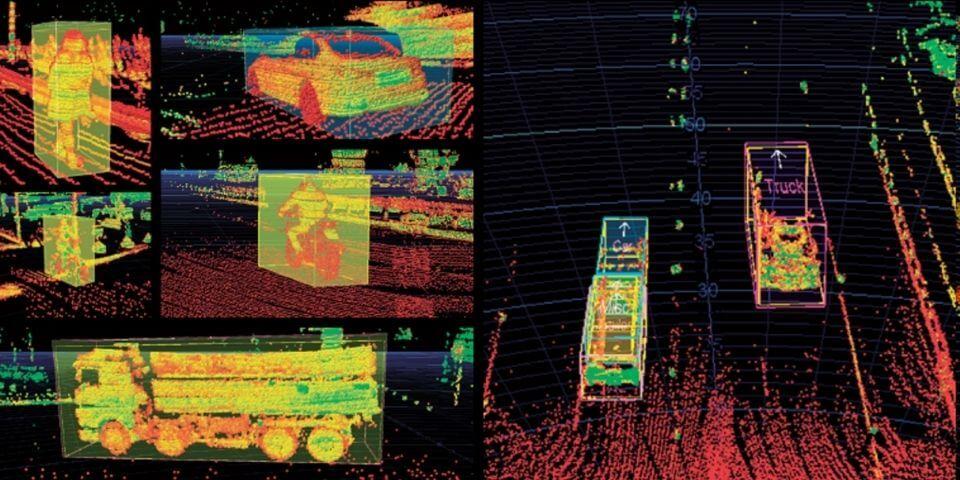
While some companies aim to achieve autonomous driving using only sensors and AI, many are working to improve safety by utilizing V2X technologies such as satellite positioning systems such as GPS, high-precision 3D maps, and vehicle-to-infrastructure (V2I) and vehicle-to-vehicle (V2V) communications.
A high-precision 3D map is a precise 3D mapping of the road and its surroundings, and various road information such as driving lanes, white lines, signs, etc. required by autonomous driving vehicles is added. A dynamic map is a high-precision 3D map that adds traffic signal information, congestion status, accident information, etc. at intersections in real time.
Based on this high-precision 3D map, the autonomous driving car identifies the position of the vehicle by matching the image projected by the sensor and GPS information, etc., and realizes accurate driving.
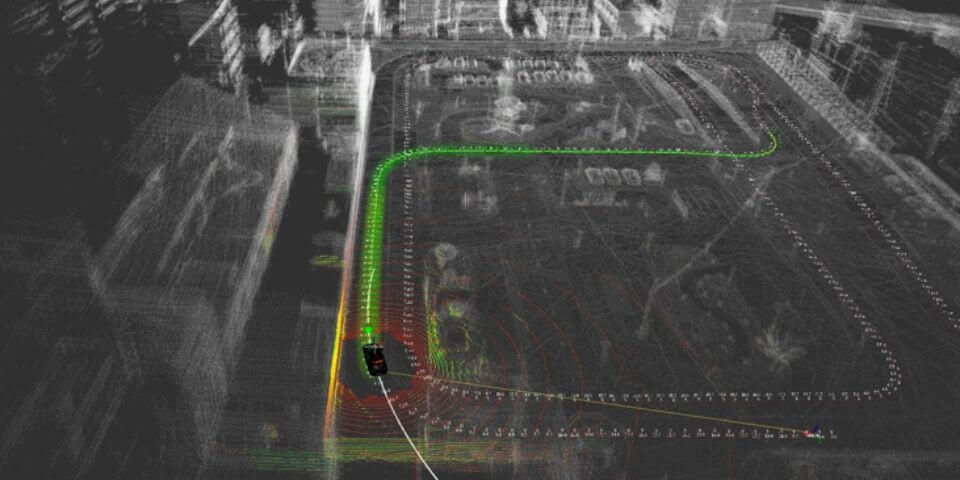
In addition, it constantly communicates with the infrastructure around the road, the vehicles running around it, the server that manages the autonomous driving system, etc., and acquires various information about road traffic, sensor data, probe data that shows the driving situation of the vehicle, etc. By exchanging data with the server, we aim to improve safety and the ability of the autonomous driving system.
In addition to this, there is also an autonomous driving system that grasps the position of the vehicle by reading magnetic markers laid on the road. This technology is expected to be put to practical use in autonomous driving services, such as fixed-route buses, where the route is decided in advance.
Elemental technologies for autonomous driving
autonomous driving cars, which combine a variety of technologies, can be said to be a treasure trove of the latest technology. The technologies that make up autonomous driving cars include AI, recognition technology, positioning technology, and communication technology, and each of these technologies is the result of cutting-edge research and development.
AI technology

AI technology plays a central role in autonomous driving. It acts as the "brain" of the vehicle, issuing control commands to the vehicle, and is widely used in each of its component technologies.
It is no exaggeration to say that the great advances made in recent years in AI learning methods, such as machine learning and deep learning, are directly linked to the realization of autonomous driving.
Recognition Technology

The development of sensors such as cameras and LiDAR, as well as the development of technology to identify what is captured in the data from each sensor, is the area of development that is attracting the most attention in the field of autonomous driving.
This is an extremely important technology because it allows the AI to determine how to control the vehicle based on the recognition results, such as improving the resolution and detection range of the sensor itself, as well as what is shown in the data, the distance to the object, its size, and what changes it entails.
Location Identification Technology
This is a technology that determines where a vehicle is currently located on the earth (road). GPS is used in car navigation systems, but it has a wide margin of error and cannot be used in places where radio waves cannot reach, such as tunnels, so it is standard for autonomous driving cars to use multiple methods in combination.
In addition to GPS, there are high hopes for the full-scale introduction of the Quasi-Zenith Satellite System (QZSS), which can provide positioning with an accuracy of just a few centimeters, as a satellite positioning system. Based on this satellite positioning system, a method of confirming the vehicle's position by comparing data on a high-precision 3D map with data displayed by on-board sensors, and SLAM technology, which can simultaneously identify the vehicle's position and create a map, can be combined to determine the vehicle's position more accurately.
Communication Technology

Currently, connected cars equipped with communication functions are becoming more and more common among privately owned vehicles, but autonomous driving cars will, in principle, be connected and will be in constant communication while driving.
In addition to sensors and AI-based recognition technology, driving safety is improved by obtaining real-time road traffic information from road infrastructure, surrounding vehicles, servers, etc. Communication with road infrastructure is called vehicle-to-infrastructure communication (V2I), and communication with other vehicles is called vehicle-to-vehicle communication (V2V), and information on intersection signals, pedestrians, driving lanes, etc. is sent and received.
In addition, by transmitting sensor data to a server, autonomous driving development companies will be able to further improve their systems. In addition, by converting collected road traffic information and vehicle information into big data, it will be possible to distribute the analysis results to each vehicle and link them to new transportation services.
The need to transmit huge amounts of data at high speeds requires communications technology that combines various communication methods, including the 5G mobile communications system.
Cybersecurity Technology

autonomous driving cars, which communicate constantly, also require advanced cybersecurity technology, because if a autonomous driving car were to be hacked, the damage would extend to human lives and the entire road transport society.
In addition to sharing security information across the industry, there is also a need for standardization of the security technologies that autonomous driving cars operating on public roads should be equipped with.
Human-machine interface technology

Human-machine interface (HMI) technology that allows humans and machines to communicate information and intentions will also be essential. Since the driver who directly controlled the car will be absent, technology will be needed to facilitate smooth communication between humans and machines, such as how to convey the intentions of the passengers to the computer efficiently and accurately, and conversely, how to convey the operation status of autonomous driving system to the passengers.
At the same time, there is a high possibility that the Driver Monitoring System (DMS), which monitors passengers, will also undergo further evolution. There is a high possibility that in-car cameras will be used to observe passenger behavior to ensure safety within the vehicle, and functions will be implemented that can understand the passengers' needs from their posture, behavior, facial expressions, etc.
Data Processing Technology

Data processing technology is essential for autonomous driving cars that handle huge amounts of data. It goes without saying that autonomous driving cars will need to have more sophisticated GPUs and storage, but it will be inefficient for autonomous driving car to process all the data by itself, so effective use of servers and clouds is required. However, it is expected that data processing delays will occur when data is processed via the cloud.
For this reason, there are moves to promote the introduction of distributed computing using autonomous driving cars at the edge and the cloud, as well as edge clouds that are positioned in between.
Benefits and uses of autonomous driving
The development of Level 4 autonomous vehicles, which will enable driverless driving, is being carried out mainly for transportation services such as buses and taxis. Although the initial cost of the vehicle itself will be high for the time being, operating costs will decrease due to lower labor costs due to the absence of drivers, which is likely to lead to lower fares in the future.
Lower fares will attract new passengers, and the spread of MaaS (Mobility as a Service), which connects various mobility services, will increase convenience, and it is expected that the number of people switching from private cars to mobility services will increase.
A reduction in the number of private cars will directly lead to the alleviation of traffic congestion and a reduction in the burden on the environment, leading to an improvement in the overall road traffic environment. It is also expected that the vacant lanes will be turned into roads exclusively for autonomous driving cars or ultra-small mobility vehicles, and sidewalks will be widened, resulting in more efficient use of roads.

Besides transportation services, the introduction of self-driving cars to delivery services is also attracting attention. While demand for home delivery is increasing due to the increase in the use of online shopping (EC), the logistics industry is facing a serious driver shortage. However, autonomous driving cars and small delivery robots can solve these problems by delivering goods unmanned.
In addition, like delivery robots, autonomous driving technology is also being used in robots that perform certain tasks within buildings, such as security, cleaning, and delivery, and they are beginning to be introduced in office buildings, shopping malls, and hotels.
In addition, the development of "flying cars" that combine drone technology with autonomous driving technology is also thriving. The main focus is on the development of electric vertical take-off and landing aircraft (eVTOL), which are larger versions of conventional drones, but there are also projects to develop a model that can both fly and drive on the ground by separating the module that drives autonomously on roads from the module that flies, and replacing the cabin that carries people.
autonomous driving law
In Japan, the Road Traffic Law, which stipulates rules for road traffic, and the Road Transport Vehicle Law, which stipulates safety standards for vehicles traveling on roads, are the main ones.
With the revision that came into effect in April 2020, "automated operation equipment" was defined, and the requirements required for level 3, such as the installation of driver monitoring functions and operation status recording equipment, were also developed. In addition, with the digitization and sophistication of technology, it is possible to update software using communication technology even in systems related to vehicle performance. In addition to expanding the maintenance of advanced technology such as operation equipment, a permission system for modifying programs incorporated in automatic operation equipment etc. has also been established.
In the future, in order to realize more advanced autonomous driving, there is a high possibility that further revisions to the Road Traffic Act, as well as revisions to the Road Act and the Radio Law will be made.

Safety standards for automated driving devices (Source: Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism "We have established safety standards for autonomous driving vehicles!")
Practical use of autonomous driving
Starting with the lifting of the Level 3 ban, which enables conditional autonomous driving, efforts to commercialize Level 4 services that enable unmanned driving have also been actively implemented in various regions.
The 2020s will be a time when automobiles based on ADAS (advanced driver assistance systems) will gradually become autonomous driving. Social implementation of Level 3 and Level 4 will soon begin in earnest, and it is likely that they will evolve and spread around 2030.
Level 3 will be in full swing in 2021
Regarding level 3 in private cars, Audi in Germany announced the level 3 autonomous driving system "Audi AI Traffic Jam Pilot" in 2017 and said that it could be installed in the flagship model "Audi A8", but legal development etc. are not in place. For this reason, it continues to be unimplemented.
In 2020, with the establishment of international standards for Level 3, automobile manufacturers have become active. In Japan, in November 2020, Honda received the world's first approval for the new model "Legend" equipped with level 3 autonomous driving functions, and Changan Automobile of China and Human Horizons have also announced mass production. . Germany's BMW and Daimler are also aiming to implement Level 3 functions through mass production and option additions within 2021.

Regarding autonomous driving buses, France's Navya sells small, low-speed EV autonomous driving buses, which are being used in practical demonstrations in Japan and other parts of the world. In Japan, autonomous driving autonomous driving that travel on fixed routes are expected to be put into practical use earlier than self the Company driving taxis, and from November 2020, in cooperation with Macnica and BOLDLY, we will begin operating transportation services on public roads in Sakai-cho, Ibaraki Prefecture. Legally it falls under Level 2, but technically it is practically equivalent to Level 3.
Level 4 is from mobile services to general passenger vehicles, aiming for commercialization in 2025
The development and commercialization of Level 4 is a situation in which Chinese companies such as Internet giant Baidu and startups WeRide, Pony.ai, and AutoX are chasing Waymo, which is leading the way in autonomous driving taxis. In addition, Uber, a major U.S. ride-hailing service company, Didi Chuxing, a Chinese company, and Aptiv, a major auto parts company, also boast a wealth of demonstration results, leading to the realization of autonomous driving transportation services ahead of automakers. We are trying to
In Japan, Nissan and DeNA are jointly demonstrating the "Easy Ride" transportation service based on the concept of free movement. In 2019, autonomous driving development startup Tier IV and JapanTaxi (currently Mobility Technologies), Sompo Japan Nipponkoa Insurance, KDDI, and Aisan Technology announced that they would start collaborating to commercialize autonomous driving taxis. In November 2020, it conducted a demonstration test of an autonomous driving taxi in Tokyo.
In the field of logistics, U.S. Nuro and China's Jingdong Group are developing autonomous driving delivery vehicles that run on roads, and U.S. Starship Technologies and U.S. Amazon.com are developing compact types that can also run on sidewalks. is in charge.
According to the "Public-Private ITS Concept / Roadmap 2020" formulated by the government, in mixed spaces such as community roads, and in limited spaces such as abandoned railway tracks and BRT (Bus Rapid Transit System) exclusive sections, safety drivers are installed at about one location each. The target is to start a service with monitoring by , and gradually expand the target, and aim to start an autonomous driving service with only remote monitoring in several places between 2023 and 2025.
For general passenger cars, based on the realization of Level 3, we expect to commercialize Level 4, which enables autonomous driving from the entrance to the exit of expressways, by 2025.
Logistics services that handle delivery are also planned to be realized after 2021 in limited areas by applying the technology of autonomous driving transportation services.
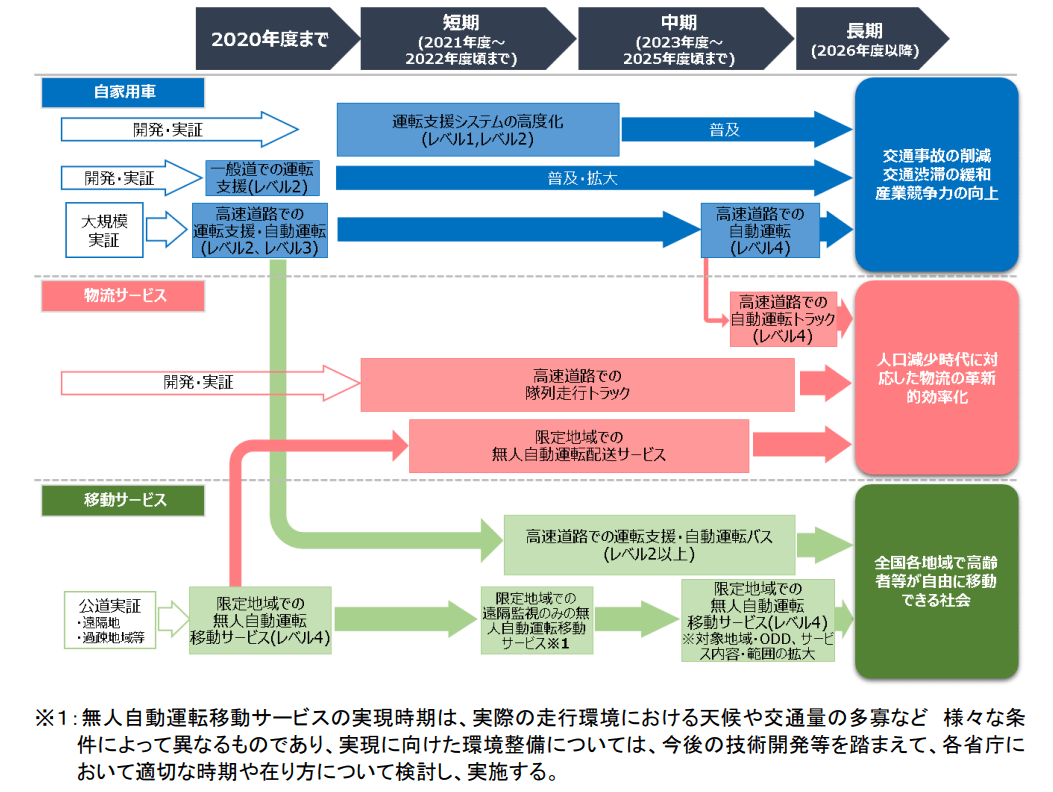
Scenarios for commercialization and service realization of autonomous driving systems (Source: IT Strategic Headquarters "Public-Private ITS Initiative/Roadmap 2020")
autonomous driving industry trends
In the past, the autonomous driving industry had formed a vertically integrated industrial structure with automakers at the top and parts manufacturers lining up.
Led by Google-based Waymo, IT and computer development companies such as Amazon, Microsoft, Apple, and China's Baidu and Alibaba have emerged as the main players, introducing autonomous driving technology to transportation and delivery services, and cloud technology. take the lead in other aspects.
Semiconductor manufacturers such as Intel and Nvidia are also increasing their presence. In 2017, Intel will acquire Mobileye, an Israeli company engaged in the development of ADAS and autonomous driving, with an estimated value of $15.3 billion (approximately 1.75 trillion yen). They acquired each for about 900 million dollars (about 96 billion yen), and are showing moves with a view to global expansion of autonomous driving transportation services.
Nvidia also announced that it had agreed to acquire Arm, a major British semiconductor design company, for $40 billion (approximately 4.2 trillion yen) in 2020. Nvidia has been developing a wide range of content and products related to autonomous driving development, and it seems to be significantly increasing its presence in the autonomous driving field.
Rise of startups and venture companies
The rise of startups is also remarkable. Companies specializing in the development of elemental technologies, such as LiDAR development and AI recognition technology, are emerging one after another, including companies that develop autonomous driving systems such as WeRide.
In the autonomous driving field, where highly specialized cutting-edge technologies are gathered, there is a strong tendency for companies in various fields to form partnerships to build autonomous driving cars, and the structure is changing from vertical integration to horizontal division of labor. Impression.
On the other hand, automobile manufacturers are also acquiring and investing in startups one after another, and there is also a movement to revert to vertical integration by bringing newly emerging players under their umbrella.
In Japan, startup ventures such as Tier IV, which develops the autonomous autonomous driving OS "Autoware", and Preferred Networks, which develops AI, are expanding their fields of activity.
CASE and MaaS
Currently, the hottest keywords in the automotive industry are “CASE” and “MaaS”. CASE is a coined word that takes the initials of Connected, Autonomous, autonomous driving & Services, and Electric, and serves as a development guideline for the industry.
Connected refers to vehicles equipped with communication functions, and even ordinary privately owned cars can be operated via smartphones, telematics insurance, enhanced entertainment functions, etc.
Sharing services refer to sharing services that utilize automobiles, such as car sharing and ride sharing.In the future, automobiles will change from being “owned” to being “shared” and “used.”

"CASE" announced by Daimler at the motor show (Source: Mercedes-Benz)
MaaS is related to the viewpoint of using this car. It means a service of transportation, and it seamlessly connects each means of transportation such as trains, taxis, buses, single-seat ultra-compact mobility and kickboards that are expected to spread in the future, and one-stop reservation and payment for use. It is an effort to improve the convenience of transit, etc. In the near future, there is a high possibility that new means of transportation will be introduced that utilize autonomous driving technology.
It is expected to appear frequently along with autonomous driving as a keyword that indicates the near future of the automobile industry and the transportation industry, so let's keep it in mind.
At the end
Currently, we are entering a transition period in which conventional automobiles are transitioning to autonomous driving. Although it may not be real yet, the revision of the law is just the beginning, and there is no doubt that the opportunities for autonomous driving cars to appear in the visible range will gradually increase.
The 2020s will see drastic changes in the traffic environment due to autonomous autonomous driving and MaaS. If we are caught up in preconceived notions, we may miss the wave of the new era. Check out the latest information and keep your knowledge up-to-date so you don't lose out to autonomous driving cars.
Inquiry
the Company, Macnica, provides a variety of products and services related to autonomous driving. If you have any questions or requests regarding autonomous driving, please feel free to contact us below.


