
Wasabi, which has a unique and refreshing flavor, is one of the essential seasonings for Japanese people when enjoying sushi made with fresh fish.
In recent years, demand for wasabi has been increasing worldwide as Japanese foods such as sushi and sashimi have become popular overseas.
It seems that many people become addicted to the unique spiciness that comes through their nose, which chili peppers don't have.
However, most of what is being sold overseas is called "horseradish" which was introduced in Europe and is also called wasabi radish, and an increasing number of foreigners are seeking genuine wasabi as it does not taste like the real thing.
As described above, while the demand for wasabi is increasing overseas, domestic wasabi production is decreasing year by year, and the market price of wasabi continues to soar in Japan, not to mention the outbound demand for wasabi.
In this article, in order to solve the problems of wasabi cultivation and pass on a rich food culture to the future, we will introduce "environmentally controlled agriculture" that aims to save labor, improve precision, and improve quality by utilizing cutting-edge technology. We would like to introduce the "Wasabi Cultivation Module", which is a small-scale plant factory built inside a container.
“I want to procure real wasabi myself.”
“I want to protect and spread Japan’s delicious crops.”
"I'm interested in a plant factory as a new business."
I hope that this will be one of the materials for your consideration.
It's actually deep! What is wasabi?
About types of wasabi
For Japanese people, wasabi is indispensable in a variety of cuisines, from Japanese to Western to French. There are two types of wasabi: ``honwasabi'', which is unique to Japan, and ``horseradish'', which is native to Europe.
Horseradish is often used in the tubed wasabi that we often eat, as well as in the powdered wasabi found in furikake and ochazuke bases.
Horseradish is characterized by a sharp, pungent taste that hits your nose, and is said to be relatively easy to cultivate as it has a strong ability to grow naturally.
On the other hand, wasabi is very delicate and grows in a rich natural environment and with the careful handiwork of people.
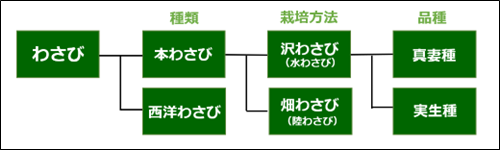
Hon wasabi can be cultivated in two ways: ``sawa wasabi'' (water wasabi), which is cultivated in wasabi fields with clear streams, and ``hata wasabi'' (land wasabi), which is cultivated in cool mountain forests.
Sawa wasabi grows large rhizomes and is eaten raw or grated. Hata wasabi grows large stems and is used for processed products such as wasabi tubes. Below, we will explain in detail about sawawa wasabi, which is often thought of as"wasabi".
Sawa wasabi is classified into two types: ``Mazuma type'' and ``Seedling type.''
Seedlings have the bright green color that is often seen in the image of wasabi, are mildly spicy, and have a refreshing taste when grated.
On the other hand, the Mazuma variety grows slowly over time, so it has a strong spiciness, aroma, and flavor, and is sticky when grated.
It is often used in long-established sushi restaurants and restaurants, and is said to have the highest quality among all wasabi varieties, making it the most highly rated wasabi on the market.
It is extremely rare and not many are available on the market, so even we Japanese have limited opportunities to taste it.
-Characteristicsof the true wife species-
・Good balance of aroma, spiciness, sweetness, and bitterness
・Strong flavor with a hint of sweetness amidst the spiciness
・It is sticky when grated
・It will not grow well unless conditions such as water quality, water temperature, soil, sunlight hours, and temperature are met.
・It is very rare because it grows slowly, taking about 1.5 to 2 years from seeding to harvest, and there is a high risk of getting sick during the process.
About the role of wasabi
Wasabi is so nutritious and has a wide variety of nutrients that it has been used as a medicinal herb since ancient times, and is said to have a wide range of health and beauty effects.
Excessive intake can put a strain on the stomach and intestines, but it is said that consuming 3 to 5 g per day is ideal.

Wasabi crisis! ? Issues and current status of wasabi
To begin with, wasabi cultivation requires clear water and cool temperatures throughout the year, as well as the need to survive Japan's hot summers twice, so production areas are quite limited in Japan.
In fact, approximately 85 % of the nation's wasabi production is concentrated in three prefectures: Shizuoka, Nagano, and Iwate, making it difficult to scale up and new entry into the industry.
In addition, in recent years, damage to wasabi fields due to natural disasters such as typhoons and heavy rains due to climate change, a decrease in the number of producers and successors due to the aging of the population, and know-how becoming individualized have become major issues, and domestic wasabi production The amount continues to decrease.
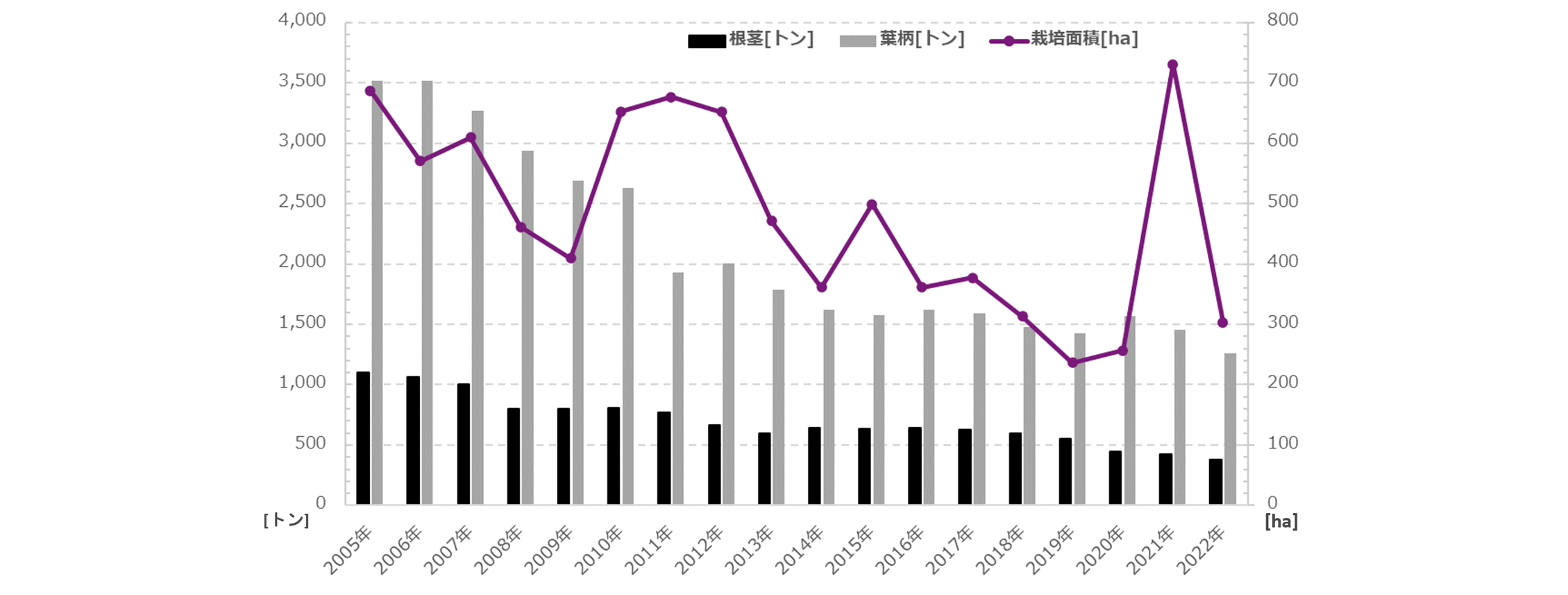
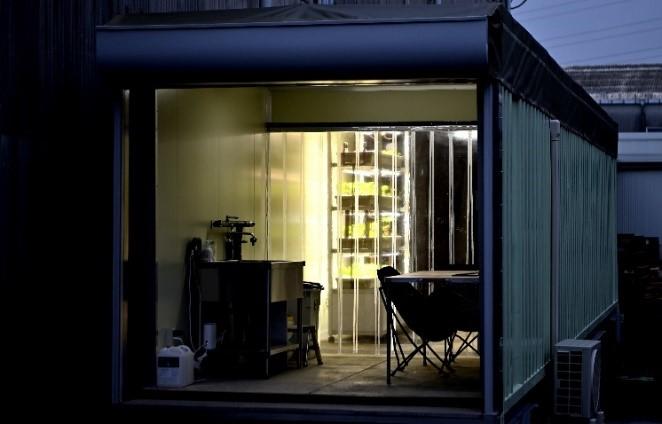
In order to protect Japan's precious food culture called "wasabi," we must create something that will allow even inexperienced people with no agricultural knowledge to reliably harvest wasabi, regardless of the environment such as climate or location. ?
With this in mind, we conducted research on technology to realize environmentally controlled agriculture and developed a plant factory that can solve the problems faced by wasabi.
What is the container-type plant factory “Wasabi Cultivation Module”?
This wasabi cultivation module was developed by NEXTAGE Co., Ltd.
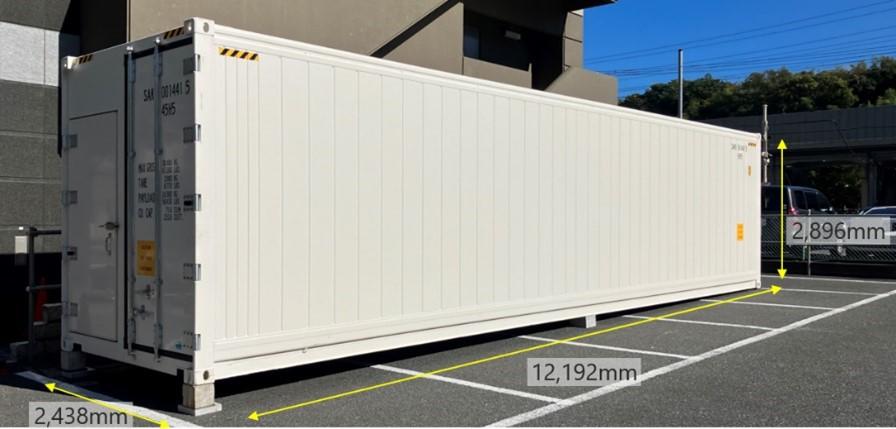
The size of the plant factory is a relatively small 40-foot container (approximately 17 tatami mats).
Rather than a large-scale plant factory, we aim to establish a production base near the areas where wasabi is needed, and to be able to supply high-quality Matsuma wasabi when needed.


Approximately 1,800 plants can be planted. The environment is controlled with LED lighting, air conditioning, water temperature adjustment, CO2 supply management, and dehumidifiers, making it possible to accelerate cultivation of Mazuma wasabi in just one year, which normally takes about two years.
Because it is grown inside a container, it is not affected by climate change or typhoons.
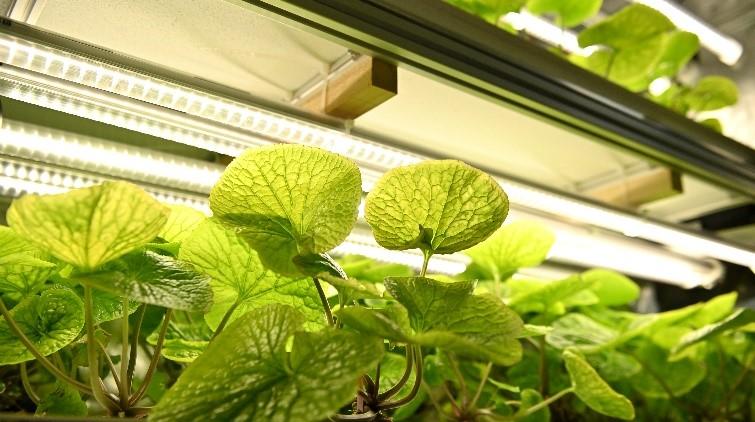

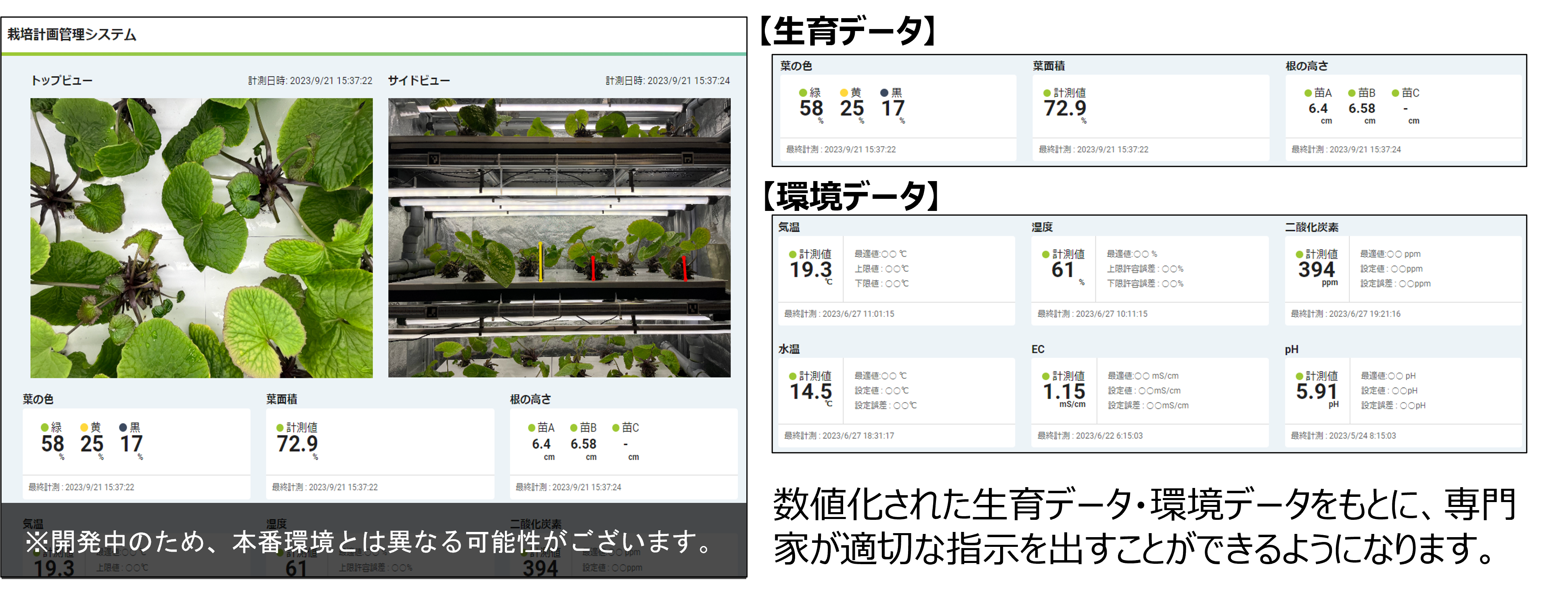
A remote monitoring system has also been installed inside the container. With this support system, including experts providing remote cultivation guidance and holding telephone conferences based on information from cameras and sensors, and a system that issues alerts if any abnormalities occur inside the container, even first-timers can grow wasabi with peace of mind.
Summary
This time, we introduced wasabi and plant factories suitable for its cultivation.
If you have read this far and would like to consider introducing our service, please contact us using the button below.
