
In its "Future Investment Strategy 2018," the Japanese government stated that next-generation mobility service MaaS would be an important measure to achieve both economic development and the resolution of regional issues. The Japanese government is working to promote MaaS while amending laws, but what is MaaS? This time, I will explain MaaS in an easy-to-understand manner.
What is MaaS
MaaS (Mobility as a Service) is a service that allows you to search for routes and transportation methods to your destination, make reservations, and make payments all at once. It is a necessary means to meet the transportation needs of each individual resident and tourist, and to solve local issues.
Seamless transportation such as trains, buses, and taxis, dispatch services (services that allow you to call taxis and ride-sharing vehicles with an app), AI on-demand buses (reservation-type shared buses without timetables or operating routes), and autonomous driving. It is a service developed with the aim of realizing a better life than connecting and owning a car.
Definition of MaaS
The definition of MaaS has a broad meaning and a narrow meaning. This is a way of thinking unique to Japan, and a narrow definition is generally used overseas.
|
broadly defined |
New mobility services utilizing IoT and AI |
|
narrowly defined |
A service that integrates multiple transportation modals and enables centralized search, reservation, and payment |
Source: Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry Study Group on New Mobility Services Enabled by IoT and AI
History of MaaS
The concept of MaaS was born in Finland in 2006, and in 2016 MaaS Global released the world's first MaaS application "Whim". Currently, MaaS is born not only in Finland, but also in the United States, Canada, Sweden, Germany, etc.
Whim, a MaaS application from Finland, a developed country
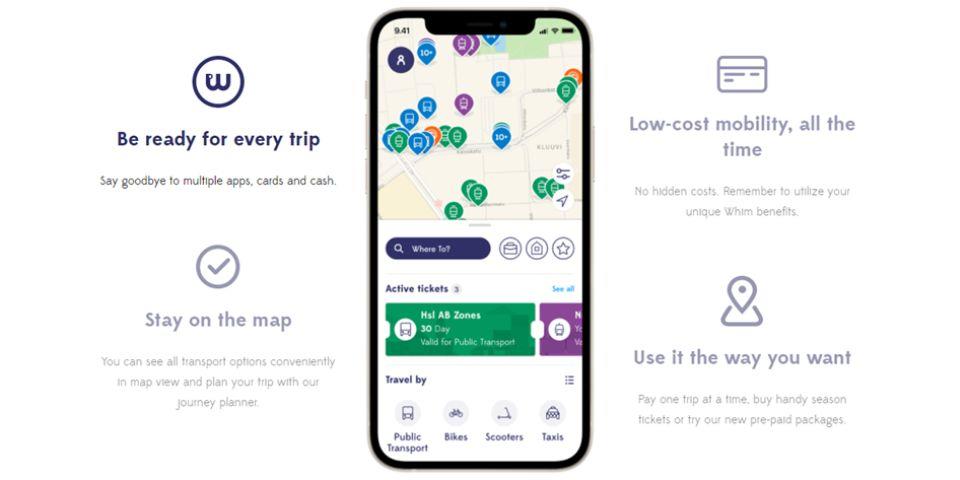
MaaS Global's MaaS app "Whim" (Source: Whim)
The Finnish MaaS app Whim is the brainchild of Sampo Hiaranen, the founder of MaaS Global. He released the service with the goal of "combining all mobility services to create a service that realizes a better life than owning a car." Whim offers unlimited rides on trains, buses, ferries, and electric scooters.
It can be used from 74.20 € (approximately 11,700 yen) per month and can be moved within the area.
Supplement: The reason why the world's first MaaS was born in Finland
The reason why the world's first MaaS was born in Finland was that it was a system that facilitated transportation reform. The Ministry of Transport and Communications is responsible for overseeing transport and telecommunications in Finland. Therefore, transportation reform was easier to proceed than in Japan, where the Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism supervises transportation and the Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications supervises information and communications. As the number of MaaS users increases, the frequency of using their own cars will decrease, which will have a negative impact on the sales of automobile manufacturers.
What can be achieved with MaaS
There are three things you can do with MaaS.
Collaboration of mobility services
By seamlessly connecting transportation services with MaaS, operator data such as operation information and ticket information are linked. By linking the data held by each business operator and consolidating it into a single application, the following mobile services can be used as a one-stop service.
- ●Railway
- ●Bus
- ● Taxi
- ● Passenger ship
- ●Airliner
- ● Green slow mobility
-
● Ultra-compact mobility
In addition, by utilizing ICT, it will be possible to provide new transportation services such as ride-hailing services, AI on-demand buses, and autonomous driving. By linking such mobility services, we will realize a more comfortable life.
"Search", "reservation" and "payment" can be done all at once
By using MaaS, you will be able to perform "search", "reservation" and "payment" for transportation services and value-added services all at once.
For example, you can make reservations for restaurants within the moving area or purchase tickets for tourist facilities. By issuing discount coupons via MaaS apps, we can aim for synergies between businesses, such as increasing the number of service users.
In this way, movement to create new businesses by finding added value in mobile services with MaaS is attracting attention.
Urban development can be done using movement data
The data collected by MaaS can be used for urban development.
For example, by accumulating data on traffic volume by time period and locations where sudden braking frequently occurs, and superimposing this data on locations where traffic accidents have occurred, it becomes easier to consider road sections and locations that require safety measures.
Also, if we can grasp the actual situation of movement, it will be easier to consider reorganizing routes on weekdays and holidays. In this way, we can work on community development while making use of movement data.
Benefits of MaaS
MaaS has seven advantages.
1. Can provide convenient transportation services
If you develop MaaS, you can provide convenient transportation services.
For example, if service users register their hobbies, tastes, and preferred means of transportation, they will be able to receive guidance on means of transportation and routes that meet their needs.
It is also possible to offer a subscription-type plan that allows unlimited rides on any vehicle within an area like Whim.
In this way, it becomes possible to provide services that satisfy service users.
2. Eliminate traffic congestion
Using MaaS to reduce the use of private cars can solve the problem of traffic congestion.
Japan is over-concentrated in Tokyo, and traffic congestion in the Kanto region has become a major problem.
In addition, traffic congestion adversely affects physical distribution, and it is said that the economic loss is as much as 12 trillion yen per year. We can solve the traffic congestion that is the source of such problems.
3. Relief for people with mobility difficulties
Elderly people often return their driver's licenses. However, in depopulated areas where there is no means of transportation, there is no choice but to rely on private cars. If you return your license, you will become a person with mobility difficulties.
MaaS is attracting attention as a service to help people with mobility difficulties. By using new transportation services such as autonomous driving and dispatch services, it is possible to help people with mobility difficulties.
4.Regional revitalization
If people with mobility difficulties can obtain a means of transportation through MaaS, they will have more opportunities to go out into the city, which will have the effect of regional revitalization.
Although there are tourism resources, it is possible to provide comfortable tourism services by introducing MaaS in areas where secondary transportation from airports and Shinkansen stations to sightseeing spots is inconvenient and it is difficult to attract tourists. If the MaaS app supports multiple languages, it will be easier to attract foreign tourists.
5. It can reduce the amount of exhaust gas from automobiles
If the number of MaaS users increases and the use of private cars decreases, the amount of exhaust gas can be reduced.
Gasoline, which is used as fuel for automobiles, transforms into substances that are harmful to humans, living things, and nature in the atmosphere, causing standby pollution such as acid rain and photochemical smog. Automobile exhaust gas is also a factor in global warming. If global warming accelerates, the temperature will rise and people will not be able to live.
Therefore, MaaS is being developed around the world to reduce the use of automobiles, reduce the amount of exhaust gas, and realize a sustainable society.
6. Optimize transportation operations
MaaS data can be monitored and analyzed in real time to optimize public transit operations. You will be able to review the operation schedule and manage the increase and decrease of flights. If you can optimize your transportation operations, you can maximize your business profits.
There is a trend toward the abolition of local transportation systems, but the movement data acquired by MaaS can also be used to integrate unprofitable routes.
7. Realize a smart city
MaaS acquires vast amounts of data on vehicle locations, passengers, and public transportation. A smart city can be realized by AI analysis of this data.
For example, real-time analysis of road congestion and the number of people using each means of transportation can be used to determine what routes and modes of transportation can be used to move around without stress.
In addition, by linking with tourist spots and commercial areas along the way, discount coupons can be distributed and event information can be notified on the app.
Level of MaaS
MaaS can be divided into five levels according to the depth of cooperation and integration of each mobile service. It was announced by a researcher at Chalmers University of Technology in Sweden, and has been adopted by the Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism in Japan as it is useful as an indicator for MaaS development. Therefore, it is a good idea to refer to this level when developing MaaS.
|
MaaS level |
Overview |
|
0 |
No integration |
|
1 |
Integration of information (transport proposals for multiple modes, price information) |
|
2 |
Reservation/payment integration (find, book, and pay for one trip) |
|
3 |
Integration of service provision (In addition to public transportation, rental cars etc. are also integrated) |
|
4 |
Policy integration (policies based on data analysis) |
level 0
Level 0 is "no integration", which means that each mobile service is not integrated and is deployed separately. Most of the current transportation systems fall under Level 0.
level 1
Level 1 is "information integration", which means that information such as fares, travel times, timetables, transportation areas, and distances for each transportation service are integrated on the platform. Route search and transit guidance services such as Jordan and Navitime Japan are representative examples of Level 1.
level 2
Level 2 is "reservation/payment integration", which means that you can "search," "reserve," and "pay" transportation services on the platform. Various transportation services can be booked and settled on the app, greatly improving convenience. moovel is a prime example of level 2.
level 3
Level 3 is “integrated service delivery”, where each mobile service is centralized on the platform and treated as one service. All mobile services in the area will be consolidated by one operator. The Whim app is a prime example of Level 3.
level 4
Level 4 is "policy integration," which refers to the stage where the national government, local governments, and business operators cooperate on the state of transportation at the urban planning and policy level. For example, transportation hubs and terminals that are necessary for connecting transportation services will be relocated to improve convenience, and new commercial and residential areas will be created in conjunction with urban development. It is a situation where efforts linked to policies are being carried out.
Issues in realizing MaaS

In order to realize MaaS, it is necessary to overcome four challenges.
Possession of legal knowledge
In the "Future Investment Strategy 2018," the Japanese government announced that MaaS will be an important measure to achieve both economic development and the resolution of regional issues. The MaaS Council was established in February 2020, and various legal revisions are being made to realize MaaS.
For example, revisions to the Road Transportation Act have permitted the use of private vehicles to transport passengers for a fee in depopulated areas, provided they are registered by the Minister of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism. In addition, the ban on taxi sharing, which was prohibited in Japan, has also been lifted.
In order to realize MaaS, it is necessary to have knowledge of such government initiatives and legal revisions. Therefore, let's check the trends of the Japanese government.
Building an ecosystem
In order to realize MaaS, it is essential to have a cooperative system of all kinds of companies, including public transportation, local governments, telecommunications companies, Internet companies, and mobility providers. Discussions can be difficult when building such a cross-industry community ecosystem. .
For example, bus companies and taxi companies may be reluctant to cooperate because they are competitors. In addition, some local governments are reluctant to adopt digital technology. Therefore, it is necessary to build an ecosystem and coordinate relationships.
Data linkage
MaaS cannot be realized without linking the data held by each business operator.
Private companies provide transportation services, and each company manages data in its own internal system, and there is no mechanism for sharing data with other companies. These data must be made open and linked.
The Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism announced an initiative to accelerate data transfer between business operators in the Interim Summary of the New Urban and Rural Mobility Service Council.
- Scope of linked data and development of linked rules
- Data format standardization
- Need for standardization and setting of API specifications
- Realization of data platform
- Use of data for the public interest, such as provision of information in the event of a disaster
Preparation for such data linkage is also an issue.
Devising service added value
When realizing MaaS in Japan, it is not possible to expect profits simply by seamlessly connecting mobile services. This is because many public transportation facilities are operating at a loss.
Therefore, we must aim for sustainable public transportation by combining value-added services such as tourism and medical care as well as transportation services to generate revenue as MaaS.
It will also be an issue to have to devise what kind of value-added services to cooperate with.
Domestic examples of MaaS
Many domestic MaaS are at the stage of demonstration experiments, but let's check what kind of efforts are being made. Here, we introduce examples of MaaS by industry.
Tourism MaaS: Yokohama Minatomirai
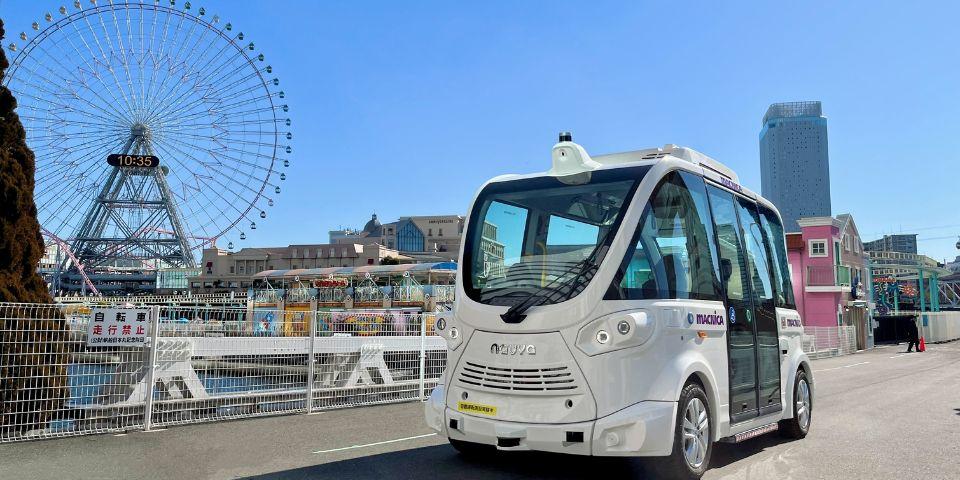

In January 2023, we conducted a demonstration experiment of "5G x autonomous driving" in the Minato Mirai 21 district. We are working on advanced urban development using ICT, such as providing sightseeing experiences using smart glasses in autonomous driving cars.
Medical MaaS: Shonan Health Innovation Park
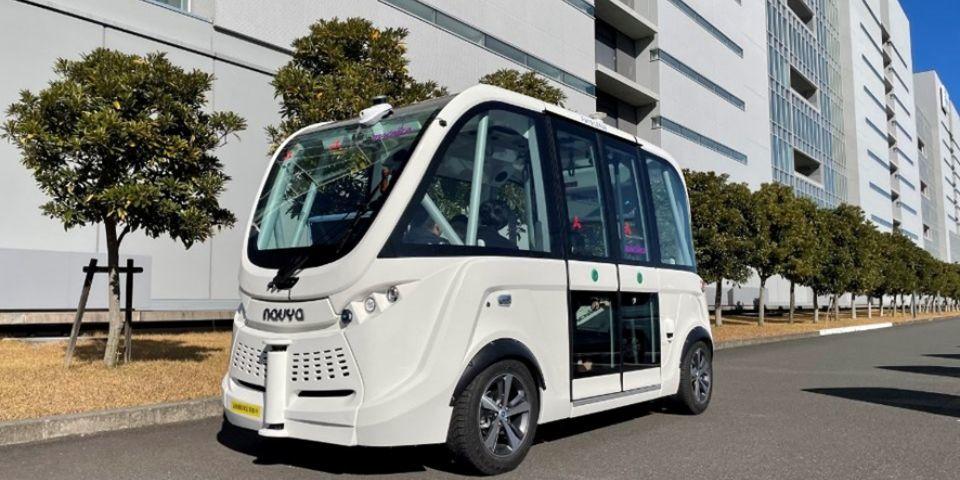

Shonan Health Innovation Park conducted a demonstration experiment for the realization of medical MaaS.
In the demonstration experiment, vital data such as electrocardiogram, blood pressure, oxygen saturation, and body temperature were measured in a autonomous driving car that assumed movement from home to the hospital, and the results were sent to the hospital for medical examination. provided. In hospitals, we aim to provide better medical services and improve the productivity of medical institutions by utilizing in-hospital transport robots and autonomous transport robots.
Logistics MaaS: Osakikamijima Town, Hiroshima Prefecture
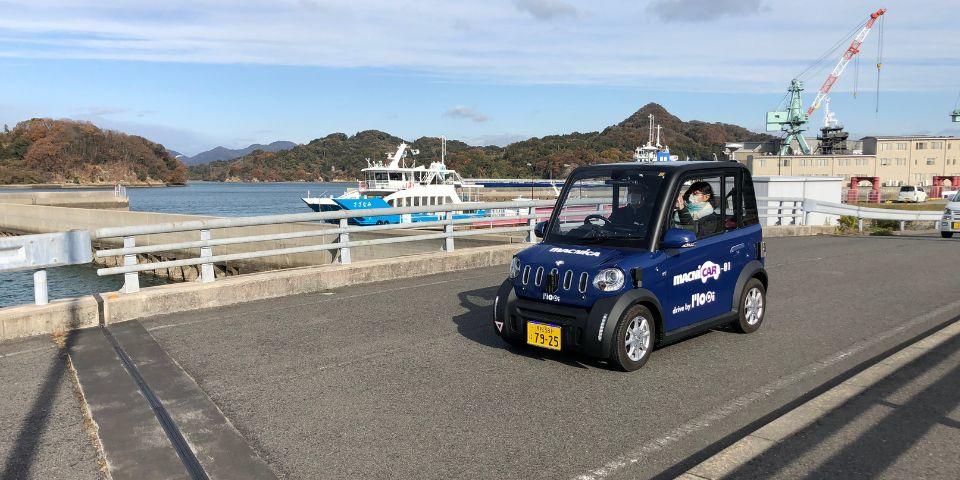

In Osakikamijima Town, Hiroshima Prefecture, a demonstration experiment was conducted using ultra-compact mobility that supports autonomous driving.
On the island, the number of elderly people (moving refugees) who returned their driver's licenses has increased, and there was a problem that it was difficult to shop. In order to solve these problems, we decided to utilize autonomous driving.
When retailers around Tarumizu Port and Shiramizu Port receive orders for goods and reserve delivery services, autonomous driving vehicles receive the ordered goods and deliver them to the orderer's home.
Although we are still at the demonstration experiment stage, we aim to create a new logistics method that supports the lives of people living on remote islands.
Summary
MaaS is a service that allows you to search for routes and transportation methods to your destination, make reservations, and make payments all at once. If MaaS can be realized, various effects can be expected, such as the elimination of traffic congestion, the relief of migrant refugees, regional revitalization, and the realization of a sustainable society. As a result, MaaS applications are appearing one after another all over the world.
Macnica is a MaaS development support company. We have a partner network of over 150 companies in Japan and overseas, and our strengths are our ability to provide total support from planning, design, and development, as well as our ability to implement cutting-edge technology.
Inquiry
If you have any questions or requests regarding MaaS, please feel free to contact us below.
