
One of the SDGs (Sustainable Development Goals) is to create a sustainable city. The maintenance and management of social infrastructure such as roads and ground structures is important for realizing sustainable urban development. However, in the maintenance and management of social infrastructure, there are various issues such as the shortage of human resources due to the high level of expertise required and the expansion of the scope of coverage due to the acceleration of aging.
Therefore, Macnica is working to solve social issues by developing "smart maintenance" that automates the maintenance and management of social infrastructure by using AI to analyze information collected from mobility sensors. In this article, we will explain how to utilize cutting-edge technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI) and autonomous autonomous driving in smart maintenance, as well as Macnica 's initiatives.
How can we realize "urban development where people can continue to live" in the face of labor shortages?
Are you familiar with the word “resilience”? Recently, it is a word that has been used frequently in the media and has the meaning of resilience, resilience, and resilience. The adjective in this word is 'resilient' meaning strong, resilient, resilient.
SDGs The 11th development goal of 2019 is to create sustainable cities and communities, and to make cities and human settlements inclusive, safe, resilient and sustainable, it is called “resilient.” The words are shown in the English representation of the target content. What is necessary to achieve the goal of “building a city where people can continue to live”?
The Japanese government has established the Basic Plan for National Resilience and is promoting various initiatives. Resilience, resilience, and resilience are especially essential in Japan, which is prone to damage from natural disasters. Japan has a lot of outdated social infrastructure, and we must urgently work on rebuilding and reinforcing them. Furthermore, from the perspective of "creating a sustainable community," in order to demonstrate "resilience," it is necessary not only to remake old things into new ones, but also to maintain and manage those social infrastructures continuously and efficiently. becomes more important.
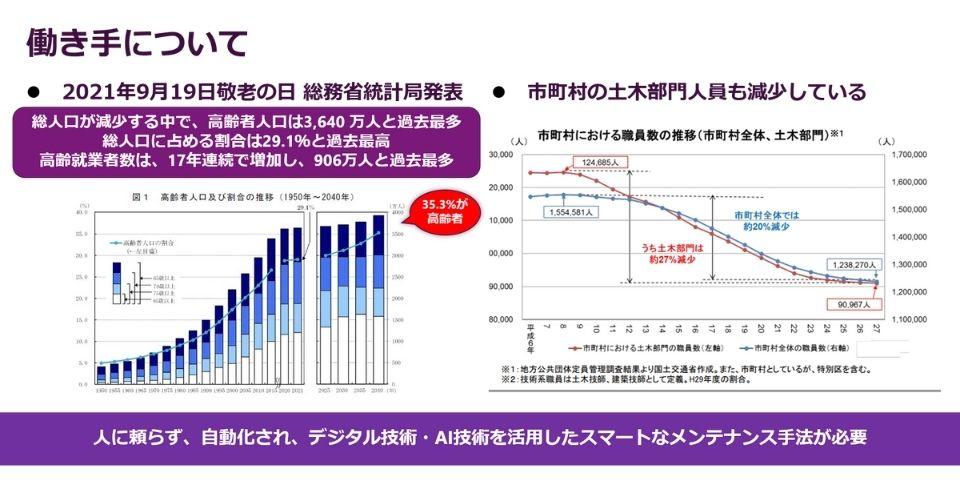
Changes in the nationwide elderly population and the number of civil engineering department employees in municipalities (Source: Statistics Bureau, Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications, Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism)
Continuous maintenance and management of social infrastructure, that is, day-to-day maintenance, has so far relied on a large number of people. But that method will no longer work. As you know, the total population continues to decline and the labor force is aging. The number of civil engineering department personnel in municipalities is also decreasing, and the aging of the population will accelerate in the future.
So what should we do? One possible countermeasure is to develop smart maintenance methods that do not rely on humans, are automated, and utilize digital and AI technologies.
Macnica 's path to realizing "smart maintenance"
Macnica has already begun efforts to put this "smart maintenance" into practice in society. One of these efforts is a system in which road information is acquired by sensors installed in autonomous driving vehicles (mobility), the collected information is stored on the edge or in the cloud, and the road conditions are analyzed using AI. If an abnormality is detected, an alert is sent along with the location information, and road surface repairs are carried out quickly and accurately.

With this mechanism, we can expect to reduce the man-hours and costs of staff by automating inspection work, and we can also improve the accuracy of inspections through AI's mechanical judgment. In addition to road surface conditions, it can also be used for maintenance of traffic signs and guardrails, early detection of obstacles, etc.
Regarding the implementation of autonomous driving vehicles and MaaS (Mobility as a Service), Macnica supports demonstration experiments and regular operation throughout Japan. We have supported Japan's first autonomous driving bus operation on public roads in Sakai Town, Ibaraki Prefecture, and public road demonstration experiments using ultra-compact mobility vehicles in Misakubo Town, Hamamatsu City, which have produced great results.
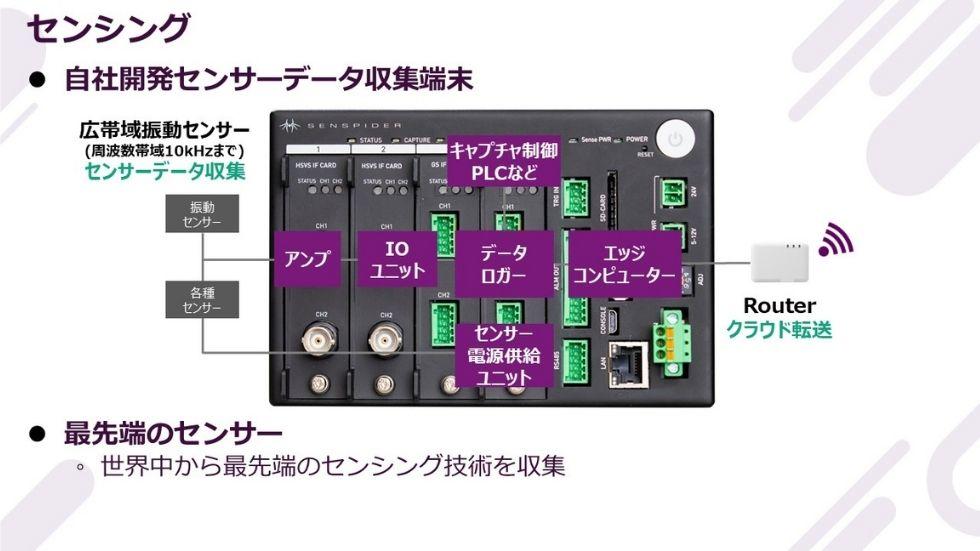
We also develop our own sensor data collection terminals. As a technology trading company, Macnica collects cutting-edge sensing technology from all over the world, and when developing devices, we develop devices that simply incorporate the necessary functions, such as sensing, data collection, and data processing before sending it to the cloud. We are developing a system that is low cost and easy to implement in society.
Furthermore, with regard to AI technology, which is evolving rapidly, we have built a specialized organization called AI Research & Innovation Hub, researching advanced AI technologies and papers around the world, and jointly developing hundreds of projects with excellent open innovation partners. I have provided consulting services to help solve problems. This organization also develops algorithms used to analyze data obtained from proprietary collection terminals.
Functions and Platform Roles of Autonomous autonomous driving /Robots, AI, and Sensing
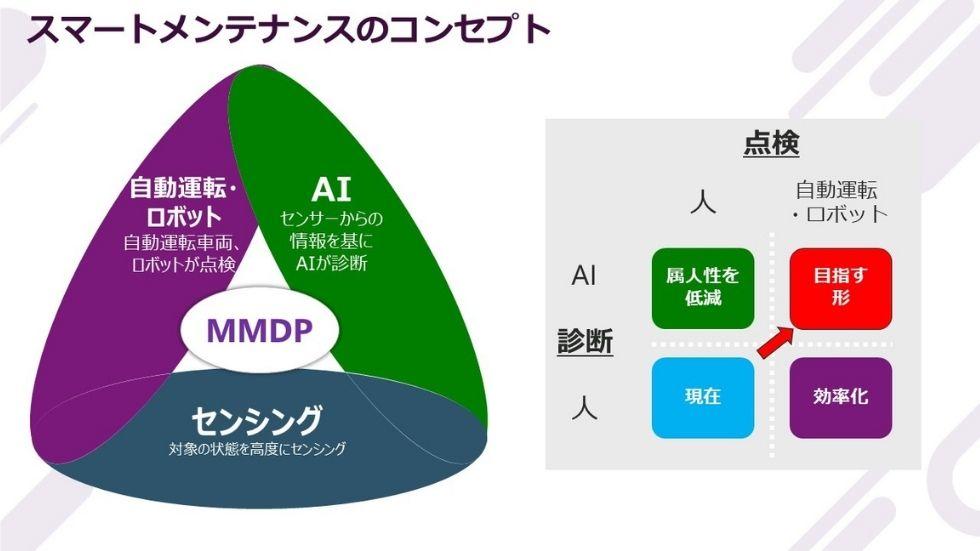
To briefly explain Macnica 's "Smart Maintenance" concept, we will advance infrastructure maintenance and management by streamlining the use of data through three technologies: autonomous driving /robots, AI, and sensing. Inspection work on roads and other areas, which is currently performed by humans, will be made more efficient by replacing it with robots, and diagnosis of road conditions, etc., which is currently performed by experienced technicians, will be carried out by AI, reducing dependency on individuals.
The Macnica Mobility Data Platform (Macnica Mobility Data Platform) maximizes the efficiency of utilizing data obtained from the functions of "autonomous driving robots," "AI," and "sensing."
This platform continuously and stably manages the entire process of transferring high-quality data obtained from various types of mobility such as passenger cars, buses, construction machinery, and agricultural machinery to the cloud, and then analyzing the transferred data. This is a system that will continue to do so. Macnica has begun applying this technology to system operation management, such as road diagnosis using autonomous driving vehicles, which we introduced at the beginning, and is responding to a variety of customer needs.
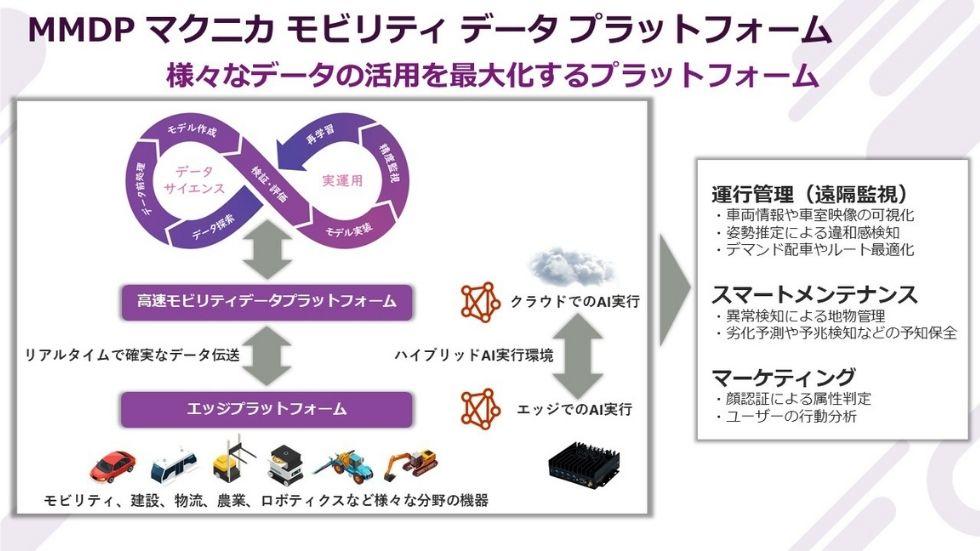
By utilizing this platform, it will be possible to centrally manage all three processes required by customers: "acquire and create data," "process data," and "use data." .
Realizing infrastructure maintenance that can be expected to save labor and speed up work
By applying this platform to road diagnosis by autonomous driving vehicles, it will be possible to monitor and understand various situations in real time.
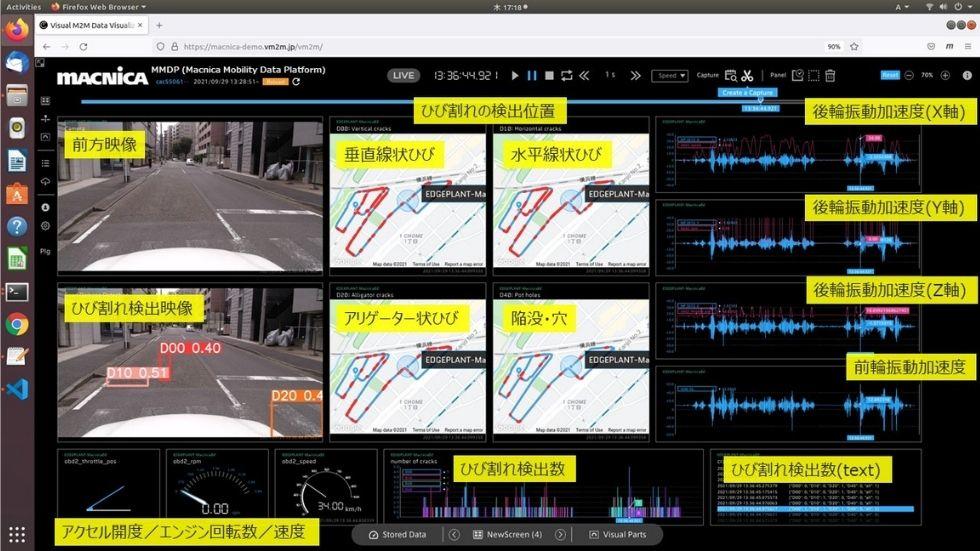
In the image above, the image of the road on which the vehicle is running is input from the camera in front of the vehicle and visualized on the screen. Then, from that screen, AI instantly judges cracks and holes on the road for each type, such as "horizontal cracks" and "vertical cracks" and notifies them.
The waveform on the right is recorded by the vibration sensor installed in the suspension of the vehicle and the vibration generated according to the condition of the road surface. The rear wheels have X, Y, and Z axis acceleration sensors, and the front wheels also have acceleration sensors to collect and record data. Of course, the position of this vibration can be accurately grasped by high-performance GPS.
These data are displayed on a map, and areas with abnormalities on the road surface are indicated in red, making it possible to visually see where maintenance is required. The map can be zoomed in to see even more detailed conditions. Since such work can be carried out remotely, it is possible to proceed quickly with a small number of people compared to the conventional situation where people got into the vehicle and worked.
Currently, it is a system that allows people to grasp this information while driving, but in the future, we will proceed with the development of new functions and responses to needs in accordance with the guidelines on autonomous driving and road inspections of the Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism. I'm here.
I hope this gave you a clear image of how in the near future unmanned, autonomous driving vehicles will be inspecting roads and maintaining an optimal road environment on a daily basis. In this way, Macnica uses advanced technology to solve problems that are familiar to us in our daily lives.
Inquiry
If you have any questions or unclear points related to this matter, please contact us from the following.
