Energy-saving Trivia "Principle of Heat Transfer"
Does heat move from hot to cold?
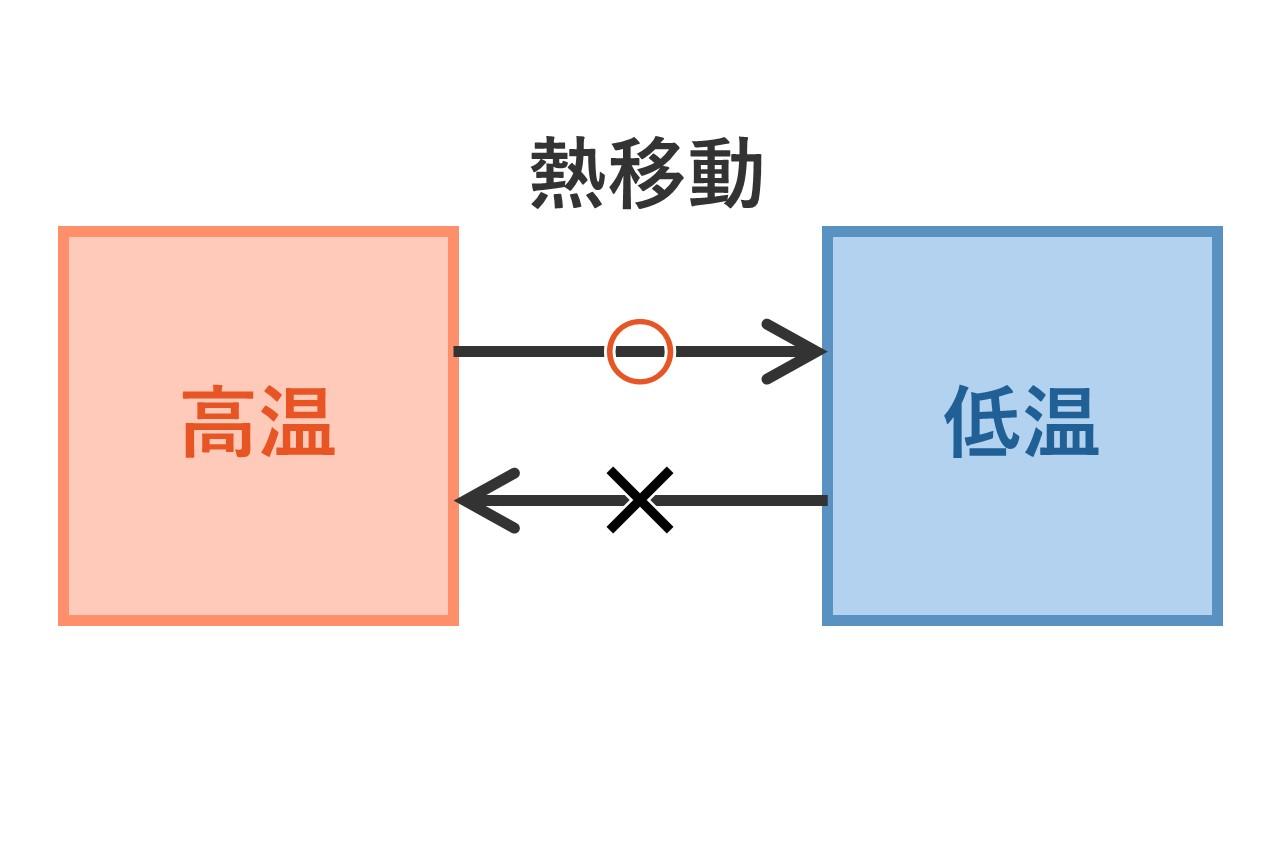
The second law of thermodynamics states that heat moves from hot to cold and does not naturally move from cold to hot.
This second law is explained by several laws such as Clausius' law and Thomson's law, so it is an equivalent law, although there are various ways of expressing it.
So why does heat move from high temperature to low temperature?
Before explaining that, it is necessary to understand what heat is in the first place.
What is heat in the first place?
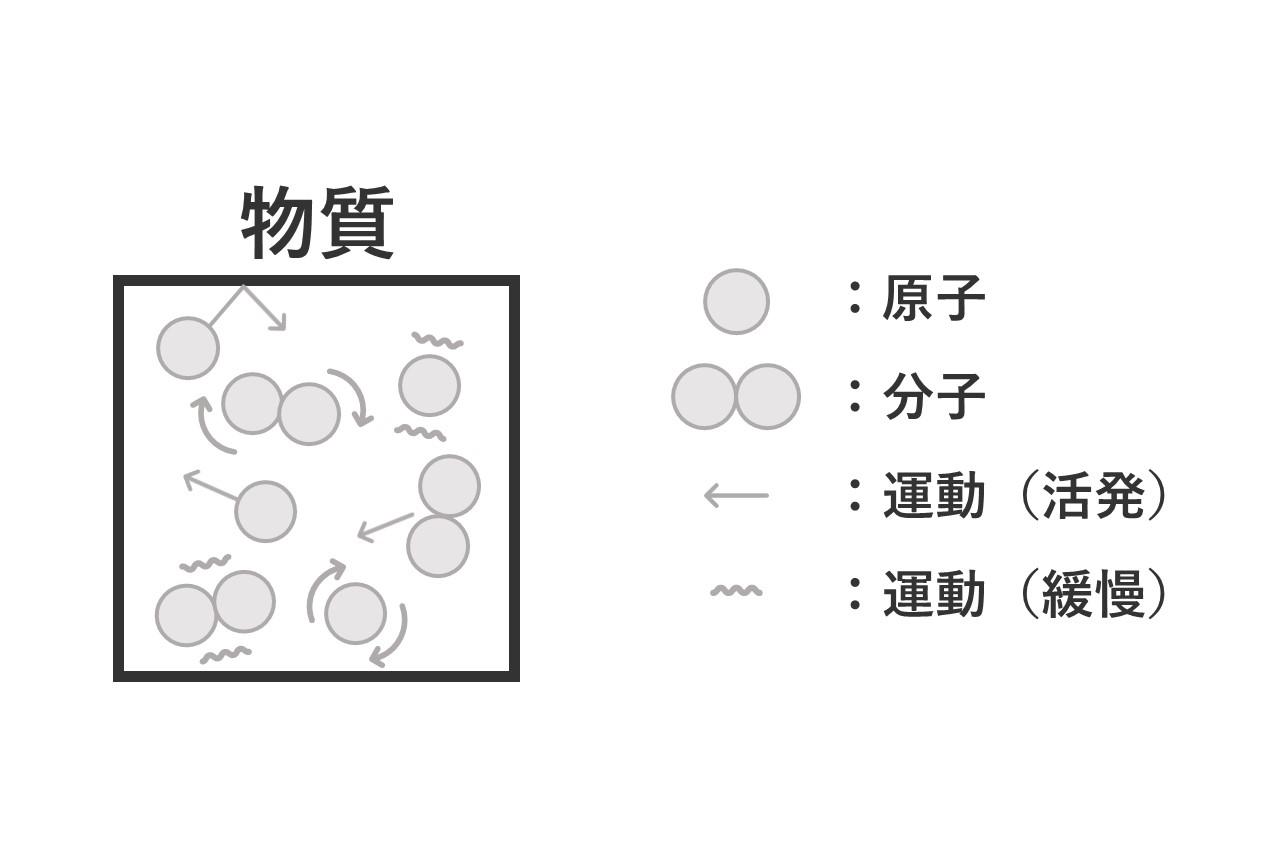
The heat emitted by an object is the movement of the atoms and molecules that make up the object.
For example, when an object is heated, the energy of the heating causes the atoms and molecules of the object to move more actively, resulting in a higher temperature.
In other words, when the movement of atoms and molecules becomes active, thermal energy increases and the temperature rises.
Conversely, when an object is cooled, the motion of atoms and molecules becomes smaller and the thermal energy becomes lower, resulting in a lower temperature. Generally, the state of absolute zero (-273.15 degrees) is the lowest value of thermal energy.
Principle of heat transfer
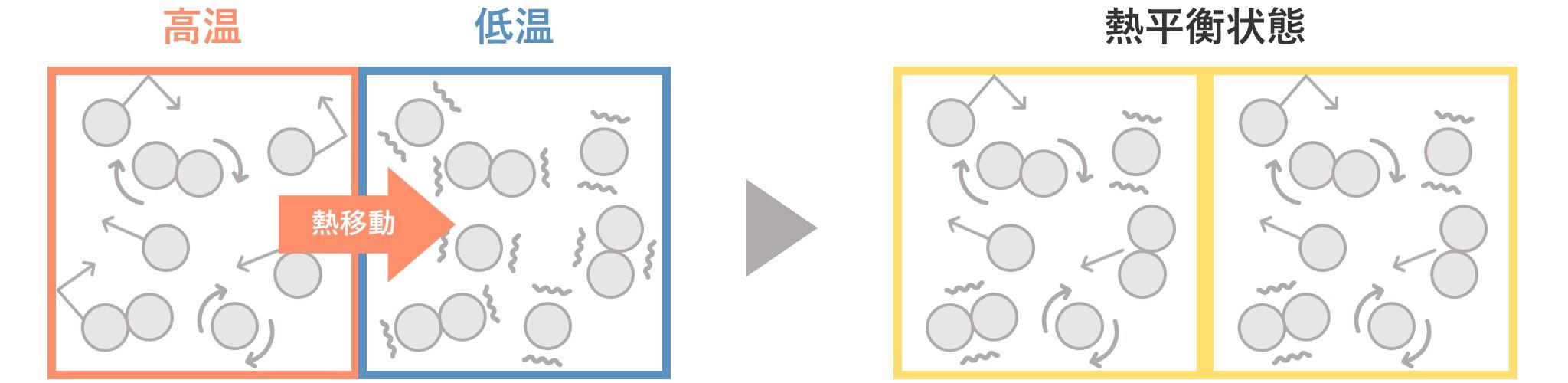
With this in mind, let's bring a hot object and a cold object into contact.
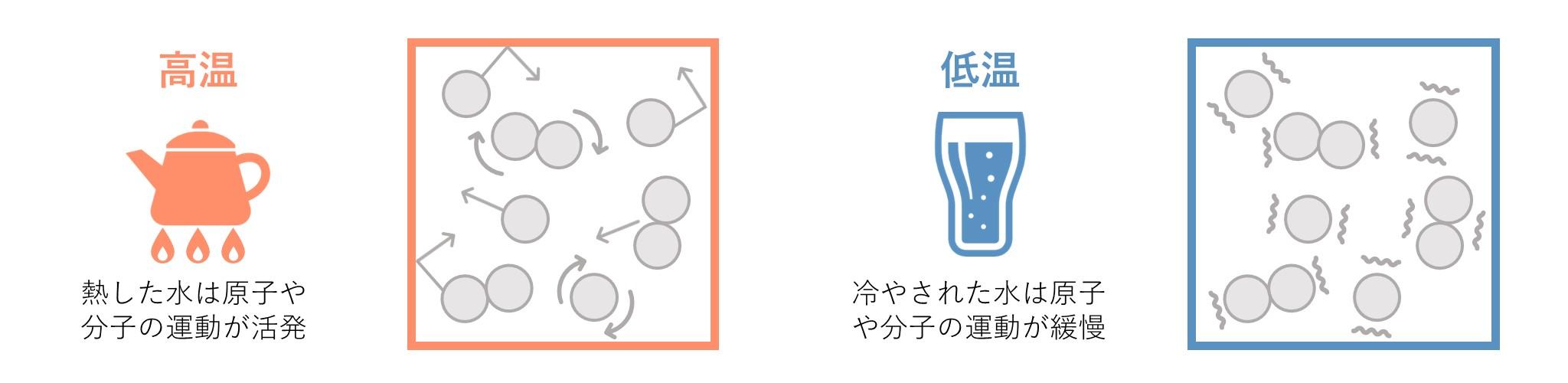
Atoms and molecules move vigorously in hot objects before contact, but atoms and molecules move slowly in cold objects.
After contact, active atoms and molecules that are moving around will gradually increase their motion by colliding with cold atoms and molecules. In other words, a cold object gradually heats up. Looking at it the other way around, energetic atoms and molecules gradually slow down as they collide. In other words, a hot object gradually cools down.
Eventually, the hot and cold objects will reach the same temperature and heat transfer will cease. This state of thermal equilibrium is called thermal equilibrium.