diode
Diode is a coined word combining the Greek word 2 (di) and electrode (electrode). Originally a vacuum tube, it was used for power supply rectification and radio detection (demodulation). Its only function was to allow current to flow in one direction only, but its size was large, just the size of a vegetable eggplant. It was also commonly called an eggplant tube.
The size has been reduced from eggplant tube → ST tube → GT tube → mT (miniature) tube. Before and after the war, ST and GT tubes were the mainstream, and I remember that the mT tube first appeared around 1955. Even the miniaturized mT tube was about the size of a human thumb, so it was large compared to its function.
Rectifying diodes were replaced with diodes using selenium called selenium rectifiers at a relatively early time. Although selenium is historically older than vacuum tubes, it is actually an image of selenium replacing vacuum tubes. For detection, it is no longer used alone in the form of living together in the vacuum tube for low frequency amplification (compound tube).
semiconductor diode
The selenium rectifier mentioned above is a diode using selenium (element symbol Se) and was used only for power supply rectification. This too has been replaced by silicon diodes due to their large size and the toxicity of selenium itself.
Diodes that appeared after selenium were germanium (Ge) diodes and silicon (Si) diodes. Germanium diodes were used in a germanium radio built by Radio Boy. Germanium has been replaced by silicon with some exceptions because the raw materials are more expensive than silicon and it is vulnerable to high temperatures.
So far, only the original rectification and detection functions have been used, but later, other functions have been used. Including for rectification, they are described below by function.
rectifier diode
It works to pass only one side of the alternating current that changes from positive to negative. In the era of bipolar vacuum tubes, the voltage to be rectified was often 200V or higher, and I didn't really care about the forward voltage (voltage drop). In terms of efficiency, I started to worry about voltage drop due to forward voltage. The forward voltage of silicon diodes is 0.7V to 0.8V, but the forward voltage of Schottky barrier diodes (SBD) is about half that, so Schottky diodes are mainly used for rectification. A Schottky barrier diode is a metal-semiconductor junction diode, as opposed to a PN junction diode. It is also used for high-speed switching due to its low forward voltage and short reverse recovery time.
SBDs were also frequently used as clamp diodes to suppress reflections during signal transmission in the TTL era. Schottky TTLs (such as 74S and 74LS) also existed with an SBD connected between the base and collector of the transistor to prevent saturation of the transistor.
zener diode
It is used to obtain a constant voltage, as shown in Fig. 1, by taking advantage of the characteristic that Zener breakdown occurs at a certain voltage when voltage is applied in the reverse direction. This breakdown voltage can be selected by the degree of doping of impurities.
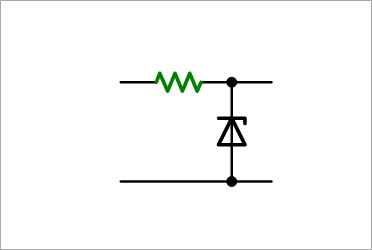
Zener breakdown is dominant for 5.6V or less, and avalanche breakdown is dominant for voltages higher than 5.6V, but the name Zener diode is used. The effect of temperature is the smallest around this 5.6V, and has a negative temperature coefficient below 5.6V and a positive temperature coefficient above 5.6V.
Photodiode
Applying a reverse bias to the diode and irradiating the junction surface with light will increase the reverse current. By detecting this current, light-to-voltage (O/E) conversion can be performed.
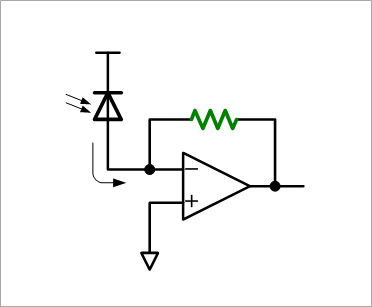
The O/E conversion circuit shown in Fig. 2 detects changes in the current of the current source (infinite impedance), so even a small amount of capacitance slows down the time response, resulting in a constant capacitance. For this reason, an electrostatic protection circuit cannot be connected, so it is a circuit that requires the most attention to countermeasures against static electricity, and in general, it seems that the O/E circuit is often housed in the package. This O/E circuit is also famous for being representative of circuits most susceptible to power supply noise. Solar cells are also included in this photodiode category.
variable capacitance diode
Applying a reverse bias to the diode changes the thickness of the depletion layer and changes the terminal capacitance with voltage. It is used in radios, televisions, VCOs, frequency synthesizers, etc., because it can change the resonance frequency by combining it with an inductor. Before using varactor diodes, variable capacitors were used. A variable capacitor is a variable capacitance capacitor that changes the degree of overlap of semicircular parallel plates, for example, by rotating a rotating shaft. It was essential for frequency tuning of radios and televisions, so I believe it contributed greatly to the miniaturization of these devices.
Light Emitting Diode (LED)
A well-known semiconductor element emits light when a forward voltage is applied to it.
esaki diode
It utilizes the phenomenon that negative resistance appears due to the tunnel effect. It is used in microwave amplifier circuits, etc.
PIN diode
An intrinsic semiconductor is interposed between the junction of a P-type semiconductor and an N-type semiconductor, and acts as a variable resistance in the forward direction and like a capacitor in the reverse direction. It is used for high-frequency signal switches, automatic gain control circuits (AGC), etc.
Although they are just diodes, they can also be used in tuning circuits, emit or receive light, or become amplifier circuits or oscillator circuits. It may have a wider function than a 3-terminal transistor.
What is Yuzo Usui's Specialist Column?
It is a series of columns that start from the basics, include themes that you can't hear anymore, themes for beginners, and also a slightly advanced level, all will be described in as easy-to-understand terms as possible.
Maybe there are other themes that interest you!
