We will explain several times about security, which is often asked in the support of Bluetooth product development.
In this fourth article, we will use Microchip's BLE module (BM70) and iPhone7 as specific examples to explain the selection of the authentication method (Association model) from the previous article, along with the actual screen display on a smartphone.
Example with iPhone7 (iOS14.4) and BM70
Below is the actual smartphone screen at Paring.
Paring is started from BM70, BM70 is Initiator and iPhone7 is Responder.
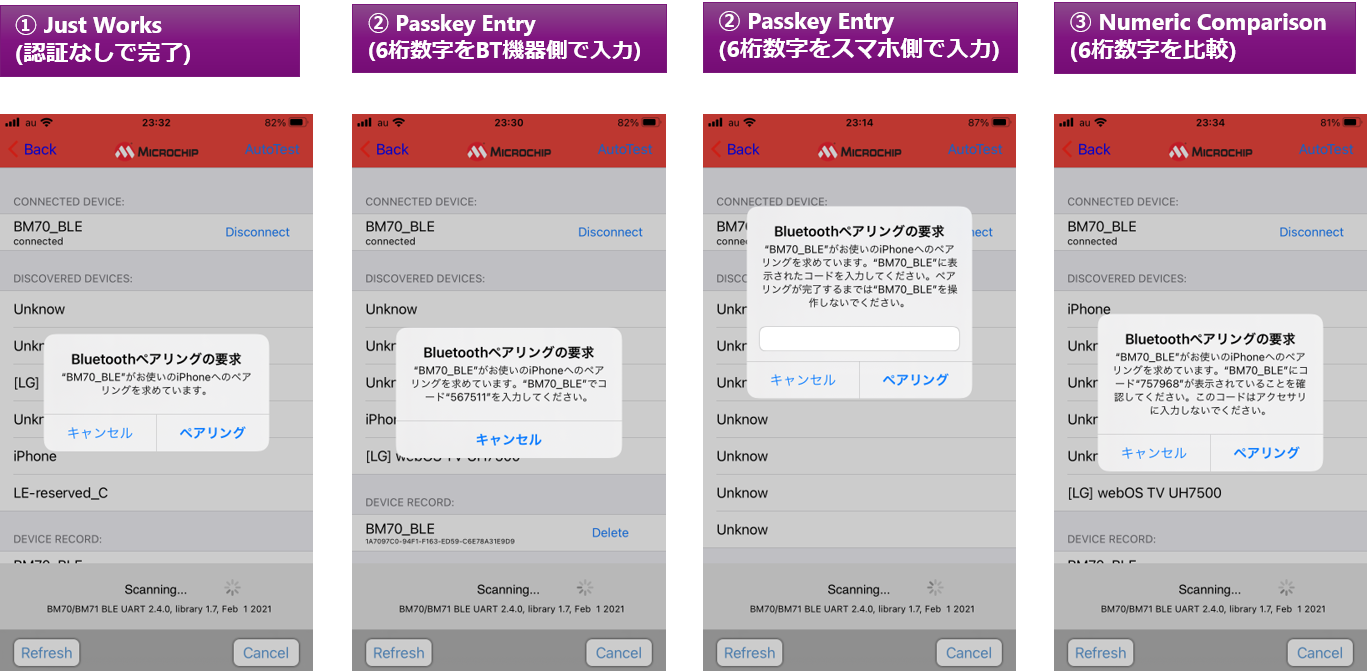
In the following, the iPhone7 screen is shown on the left side, and the PC UART command transmission/reception Tool screen that substitutes for the Host MCU is shown on the right side for a more detailed explanation.
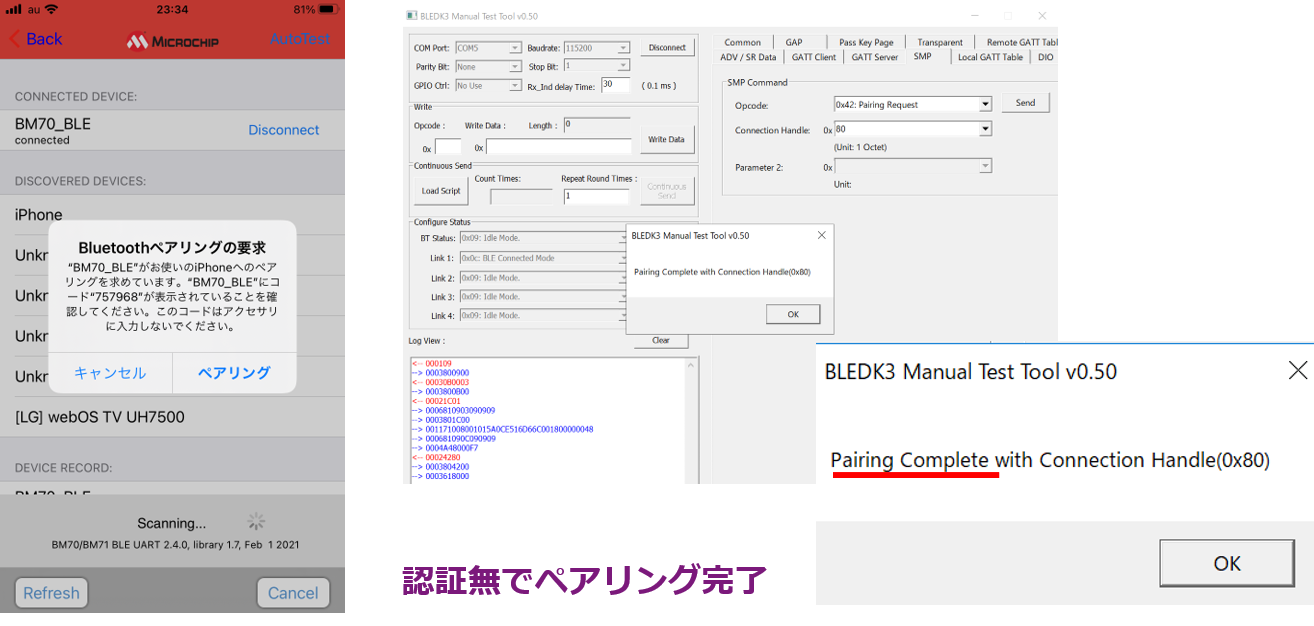
Method ① Just Works
This is an authentication method for devices without input/output, such as BT earphones and speakers.
Encrypted communication with public key cryptography is possible, but there is no public key authentication and no security resistance to man-in-the-middle attacks.
*The BT earphone/speaker uses Classic BT instead of the BLE introduced in this example.
Although there are minor differences, Classic BT also has an authentication method similar to BLE, and the Just Works method is adopted.
(In the future, in addition to Classic BT, we expect to release earphones that use BLE Audio, which was added in BT5.2 in 2020.)
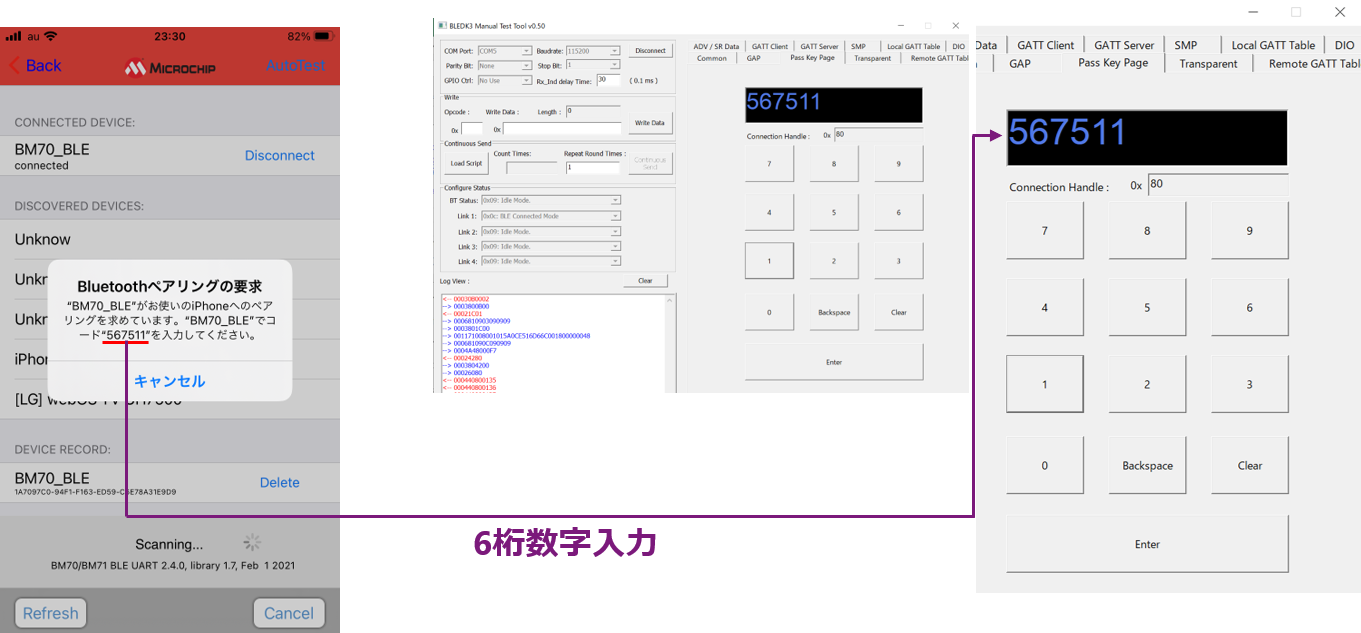
Method ② Passkey Entry
This is an authentication method that can be selected for devices that can enter 6-digit numbers.
Has security resistance to man-in-the-middle attacks.
One side displays a 6-digit number and the other side is a method for entering a 6-digit number, so there are two ways to enter it.
In this case, the first is a BLE device (BM70) and the second is an example of entering a 6-digit number on a smartphone.
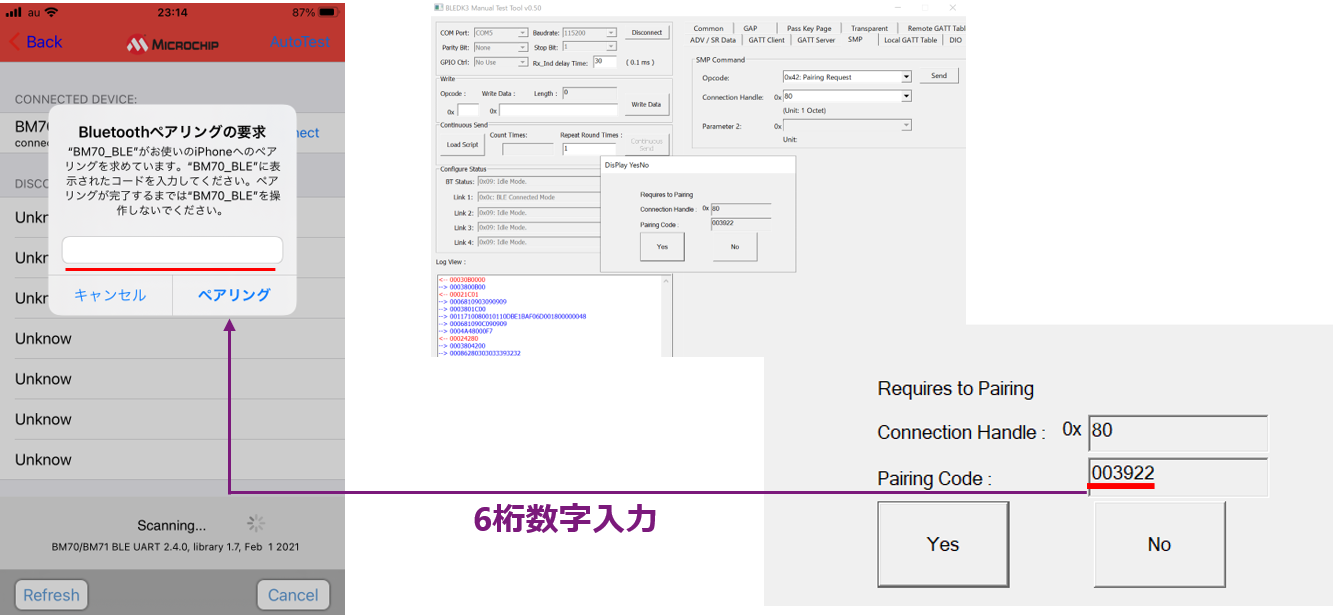
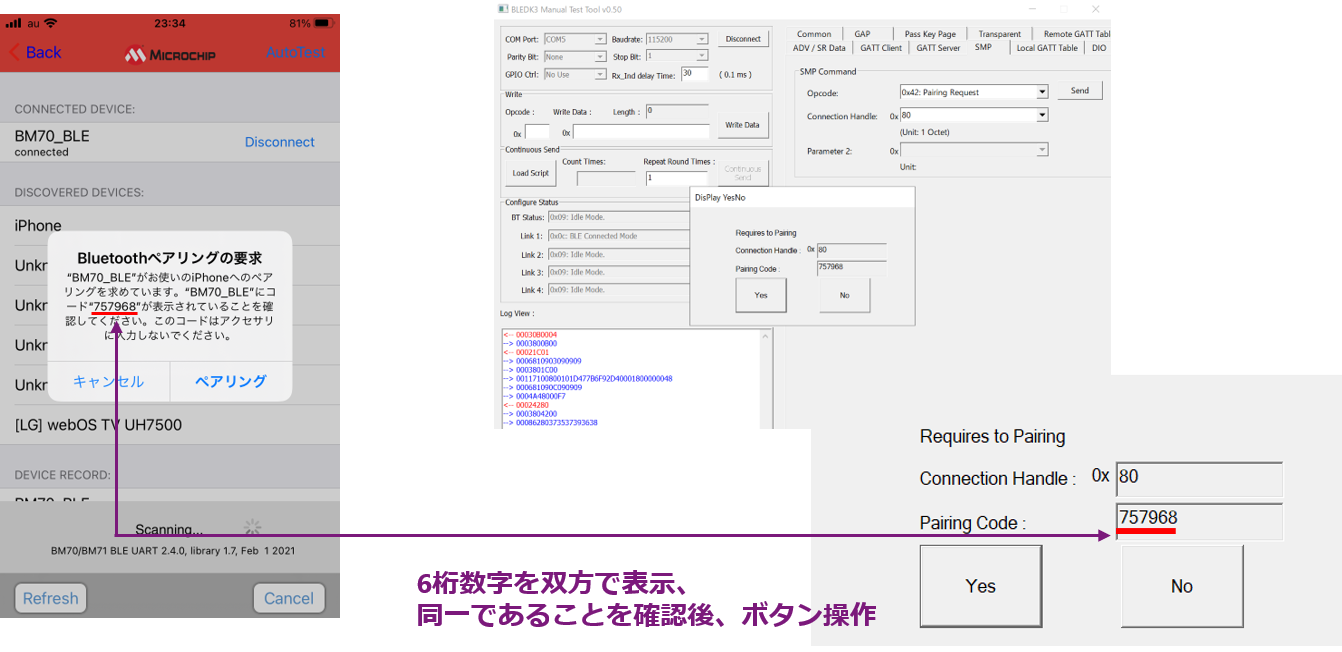
Method ③ Numeric Comparison
This authentication method displays a 6-digit number on both devices and compares it to confirm that it is the same.
Has security resistance to man-in-the-middle attacks.
If both display and Yes/No button operation are possible, it can be selected.
Since it simply compares numbers and operates Yes/No buttons, the load on the end user is not so high.
It has security resistance against man-in-the-middle attacks, so it is recommended that you consider including it as an option for products that require high security.
Summary
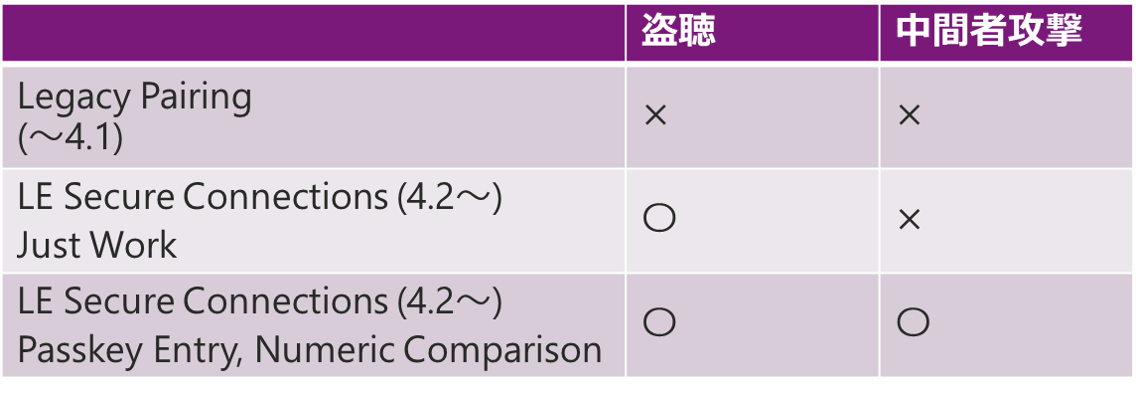
Compared to Legacy Paring before BT4.1, BT4.2 and later LESC introduces a public key cryptosystem to improve security resistance against eavesdropping.
Regarding public key authentication, there are multiple authentication methods, the simplest Just Works method that does not perform authentication, and the Passkey Entry, Numeric Comparison method that authenticates using a 6-digit number.
If your product requires high security and can be equipped with a display and buttons, please consider Numeric Comparison method as an option that can achieve both usability and security.
Inquiry
If you have any questions regarding this article, please contact us below.
To Microchip manufacturer information Top
If you want to return to Microchip manufacturer information top page, please click below.
Free online seminar
If you know this, you can develop Bluetooth products! Seminar for Bluetooth Beginners
