Low Pass Filter
The Low Pass Filter has the role of smoothing the output of the phase comparator and the role of compressing Jitter. The filter time constant affects the time it takes for the PLL to stabilize. This is because the time constant determines the Filter's response characteristics. One of the PLL metrics that includes the time constant is the damping factor. A normal PLL is designed to set the damping factor to a value on the order of √2/2. Even if the stabilization time is long, a large damping factor may be used to make it difficult for the PLL to get out of lock.
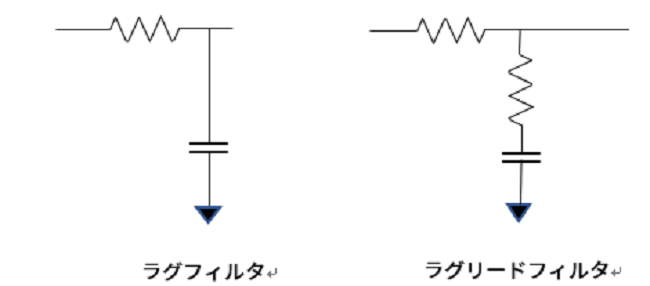
A lag filter does not return the phase to a phase lag, but a lag-lead filter can lead/lag the phase and have a phase margin. However, since we cannot obtain attenuation in the high frequencies, we end up constructing 2nd or 3rd order filters. Normally, a lag filter is configured after the lag-lead filter to compensate for attenuation in the high frequencies. When designing a broadband PLL, if the gain is insufficient with the above passive filter, an operational amplifier can be used to increase the AC gain.
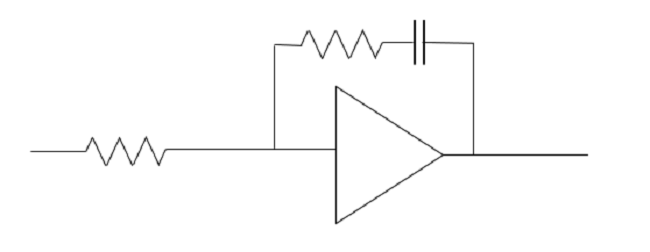
Giving a filter a gain also affects Jitter compression by the filter. The filter cutoff frequency must be determined in consideration of the phase comparison frequency and the Jitter frequency superimposed on the Reference Clock. By using a high-order filter, it is necessary to improve the Jitter compression effect in the high range.
Next time, I will describe the frequency divider circuit.
Inquiry
For inquiries and questions regarding this article, please use the button below.
To Microchip manufacturer information Top
If you want to return to Microchip manufacturer information top page, please click below.
