Integer 分周回路
Integer 分周回路は整数分周、つまりVCOの出力周波数が、PLLのReference 入力の整数倍である必要があります。例えば入力のReference Clock入力が10MHzでVCOの出力が100MHzだった場合、1/N分周回路は10分周すればよいことになります。
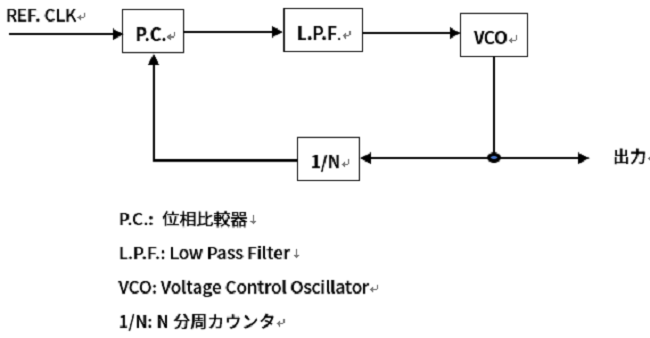
Fractional 分周回路
Fractional分周回路は、VCOの出力をPLLのRefrence Clock入力で割り切れない場合に使用します。簡単な例としてReference Clock入力が21MHz、VCOの出力が100MHzの場合を考えてみます。最大公約数は1MHzとなり、整数分周でもPLLの構成は可能です。PLLの閉ループゲインを上げるために直接Reference Clock入力を使用してPLLを動作させたいケースを考えます。この場合、1/N分周回路は整数での分周ができず、小数点分周が必要となります。5分周4回と4分周1回の組み合わせによって、100MHzから21MHzを生成することは可能です。ただし、回路の作りやすさを考えて5分周4回の後に4分周1回を持ってくるとFractional Spuriousが発生してしまいます。5分周を4回、4分周を1回とすると21MHzの5clock周期でパルス幅の短い周期が発生し、4.2MHz(21MHzの1/5)がJitterとして重畳されているのと同様になります。
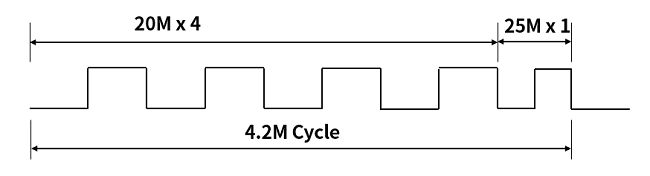
定期的ではなく、ランダムに4分周を挿入することによってFractional Spuriousは分散されSpread Spectrum Clockと同様になり、また、LPFのCut Offを重畳したJitterを抑圧する周波数に設定することによってJitterはある程度抑えることが可能となります。
次回は、JitterとWanderについて記載します。
お問い合わせ
本記事に関してのお問い合わせ、ご質問は、以下のボタンからお願いします。
Microchip メーカー情報Topへ
Microchip メーカー情報Topページへ戻りたい方は、以下をクリックください。
