Inductors and capacitors are essential components in electronic circuits. I will explain the basic role of its operation.
The contents of this time will be Part 4 "What is a capacitor?"
If you want to see other articles, there is a summary page, so please take a look there.
Overview
Along with resistors and inductors, it is one of the representative passive components. The circuit symbol is "C" and the unit is "F"(Farad).
Some engineers call it a capacitor or a C, but you can basically think of it as a synonym.
The circuit symbol is shown like this.
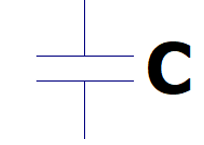
The main uses are as follows.
・Storing / discharging electric charge
・Remove noise
・Stabilize the voltage
Structure and charging behavior
Describes the basic structure and charging operation of a capacitor.
Figure 1 shows the basic structure of a capacitor, in which a dielectric is sandwiched between two electrodes.
Figure 1 Capacitor structure
Figure 2 shows the charging behavior of a capacitor.
When a voltage is applied to the electrodes, electricity flows in and accumulates positive and negative charges. The charge builds up over time and stops flowing when the voltage between the electrodes becomes the same as the applied voltage.
Once the charge is stored, the state will be maintained even if the voltage is removed. When a load such as a resistor is connected, it will discharge until the charge disappears.
Figure 2 Capacitor charging operation
Figure 3 shows the charge waveform when a 5 Ω resistor is inserted between a 5 V voltage source and a 100 μ F capacitor.
It can be confirmed that the current decreases as the voltage of the capacitor rises, and the applied voltage rises to 5V.
Figure 3 Capacitor charging waveform
The symbol for the accumulated charge is Q, the unit is C (coulomb), and it can be calculated by Q=CV, so the charge in the charged state is like this.
Q=100μ [F] × 5[V]
=500μ [C]
1C (coulomb) is the amount of electricity carried in 1 second by a constant current of 1A, so if 1A is applied at 500μ [C], it will be discharged in 500μs.
Capacitance of capacitor
This section describes how to calculate the capacity of a capacitor.
Fig. 4 shows the formula for calculating the capacitance of the capacitor.
The capacitance is determined by the area of the electrodes used, the permittivity of the dielectric, and the distance between the electrodes.
Figure 4 Capacitance calculation formula for capacitor
When actually using a capacitor, not only the capacity but also the rated voltage and size are taken into consideration, so it is necessary to select a capacitor that is suitable for the application from types such as aluminum electrolytic capacitors and ceramic capacitors.
The types and characteristics of capacitors will be explained in the next section.
Information on simulation tools
Inquiry
If you have any questions regarding this article, please contact us below.
Click here to buy now
Wurth Electronics Manufacturer Information Top
If you would like to return to the Wurth Electronics manufacturer information top page, please click below.
