In the previous article, we introduced the types and features of semiconductor temperature sensors. In Part 3, we will introduce usage examples from the reference design and reference materials for future developers.
Types and Characteristics of Temperature Sensor Series
Part 1 Characteristics of thermocouples, RTDs, and thermistors
Part 2 What is a semiconductor temperature sensor?
Part 3: Application Examples of Semiconductor Temperature Sensors
Application examples of semiconductor temperature sensors
Semiconductor temperature sensors are mainly used in the following three applications.
- Continuous temperature measurement
- Abnormal behavior detection
- Replacement from RTDs and thermistors
Concrete usage example
- Internet of Things (IoT) sensor node
- Replaces industrial RTDs (Class AA) or precision NTC/PTC thermistors
- medical/fitness equipment
- medical thermometer
- human body temperature monitor
- Metering temperature compensation
- Environmental monitoring and thermostats
- wearable
- Asset tracking and cold chain
- gas and heat meters
- Test and measurement equipment
- RTD alternatives: PT100, PT500, PT1000
- Thermocouple Cold Junction Compensation

Reference design using semiconductor temperature sensor
I would like to introduce four types that I would especially recommend among those published on the website of Texas Instruments (hereafter TI).
- Focused on low power consumption: low power temperature digital meter
- For machine vision: LED lighting control
- Medical/wearables: human skin temperature sensor, wearable applications
- Automotive: Automotive high temperature sensor
Focused on low power consumption: low power temperature digital meter

Overview
- Thermometer using ultra-low consumption microcomputer [MSP430]
- Approximately 0.2mW power consumption during operation. Button battery allows long-term operation
- Accuracy of ±0.2°C from -10°C to 85°C
- Available (Purchase here)
Click here for details of this reference design
http://www.tij.co.jp/tool/jp/TIDA-01626
Notes
Writing a program to the MSP430FR5969 requires a tool like MSP-FET.
http://www.tij.co.jp/tool/jp/MSP-FET
For the connection method, refer to P41 of the document below, VCC, GND, TDO/TDI, TCK
It will be in the form of connecting the four terminals of
MSP Debuggers User's Guide
For machine vision: LED lighting control
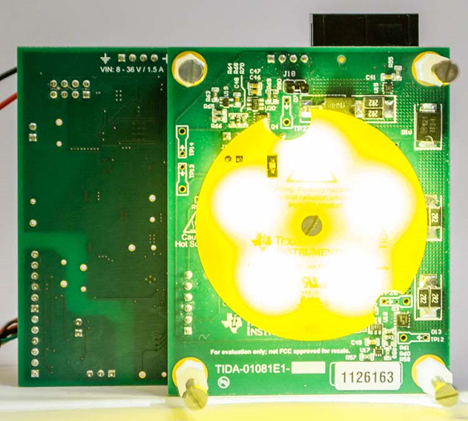
Overview
- Camera illumination or flash for imaging using high-brightness LEDs
- Use TMP116's ALERT feature for temperature monitoring of LEDs with up to 2.4A current (up to 70°C)
- Capable of quick protection operation when temperature abnormality occurs
Click here for details of this reference design
http://www.tij.co.jp/tool/jp/TIDA-01081
Medical/wearables: human skin temperature sensor, wearable applications

Overview
- Introducing a method to mechanically attach a temperature sensor to accurately measure skin surface temperature
- Layout Considerations for Thermal Path Routing to Achieve ±0.1°C Accuracy
- Design example of an ideal mechanical case for mounting
Click here for details of this reference design
http://www.tij.co.jp/tool/jp/TIDA-00824
Automotive: Automotive high temperature sensor
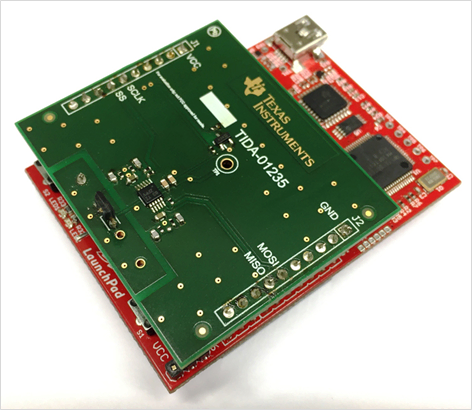
Overview
- Combination of thermocouple and temperature sensor
- High Density, Low Cost, Accurate Thermocouple AFE Circuit
- Design specifications for –40°C to 1300°C (thermocouple temperature range) and ±1°C accuracy
Click here for details of this reference design
http://www.tij.co.jp/tool/jp/TIDA-01235
Reference material
Temperature measurement circuits centered on RTDs in various devices will change at an accelerated pace in the future with the advent of semiconductor temperature sensors. TI publishes useful materials for designing for those who are considering new introduction of semiconductor temperature sensors.
For those considering replacement
Replacing RTDs in Precision Sensing and Compensation Systems Using Digital Temperature Sensors
http://www.tij.co.jp/general/jp/docs/lit/getliterature.tsp?baseLiteratureNumber=snoaa06&fileType=pdf
An example of changing from an RTD to a semiconductor temperature sensor is described. The circuit block, which has been essential for RTDs so far, is no longer necessary, resulting in a very clean circuit configuration.
Design considerations
Temperature sensor PCB design guidelines
http://www.tij.co.jp/general/jp/docs/lit/getliterature.tsp?baseLiteratureNumber=snoa967&fileType=pdf
This paper provides system designers with recommendations on how to improve the accuracy of the measured temperature points. It also describes layout techniques, device orientations, and the most efficient implementation techniques.
Design considerations for measuring ambient air temperature
http://www.tij.co.jp/general/jp/docs/lit/getliterature.tsp?baseLiteratureNumber=snoa966&fileType=pdf
Design know-how on the heat capacity of the substrate and evaluation method when using the semiconductor temperature sensor is described. This is the most important document to read.
Layout Considerations for Wearable Temperature Sensing
http://www.tij.co.jp/general/jp/docs/lit/getliterature.tsp?baseLiteratureNumber=snia021&fileType=pdf
Unlike ambient temperature measurement, human body temperature measurement requires high followability. This document describes the know-how regarding body temperature measurement using LMT70 and TMP117.
Accurate temperature measurement with TMP116
http://www.tij.co.jp/general/jp/docs/lit/getliterature.tsp?baseLiteratureNumber=snoa986&fileType=pdf
Experiments have been carried out to determine how the power supply voltage and substrate material affect the measured temperature, and the data are shown.
Please feel free to contact us if you have any questions about selecting semiconductor temperature sensors.
For inquiries about the reference designs of the products introduced this time or the products used in the reference designs, please use Macnica Online Service inquiry form.
Also, if you have any trouble selecting a semiconductor temperature sensor or replacing an existing product, please feel free to contact us. Our engineers will assist you in your selection.
Click here for recommended articles/materials
Types and Characteristics of Temperature Sensor Series
Part 1 Characteristics of thermocouples, RTDs, and thermistors
Part 2 What is a semiconductor temperature sensor?
Part 3: Application Examples of Semiconductor Temperature Sensors

