"Motors" that give movement to products are used in a wide variety of applications such as robots and printers.
There are various types and functions of "motor drivers", devices that support the motor behind the scenes.
In the first half, when starting product development using a motor, we will introduce the points of how to choose for those who have a question, "How should I choose a motor driver?"
In the second half, we will introduce a relatively new recommended motor driver evaluation board from Texas Instruments (hereafter TI) that our engineers have carefully selected.
What is a motor driver in the first place?
A motor driver is a device that drives and controls a motor. It controls the amount, direction, and timing of the current that flows through the motor, and protects the device in the event of an abnormality.
The types of motors are broadly divided into
- ac motor
- DC motor (Brushed/Brushless)
- stepper motor
classified as
Since the drive method and circuit differ depending on the type of motor, it is necessary to select a motor driver that matches the motor.
How to choose a motor/driver
So what should we consider first when choosing a motor driver?
First, when the development application and specifications are determined, the type of motor and the type of motor/driver are determined. From there, you can select the most suitable device by selecting the detailed specifications of the motor/driver.
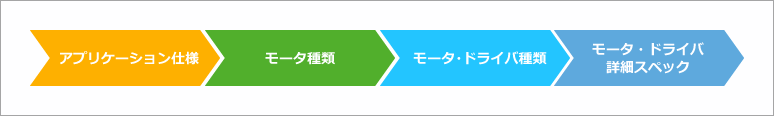
Determination of motor type and motor/driver type
Once the application specifications are determined, you can easily determine the type of motor and motor/driver simply by answering three questions.

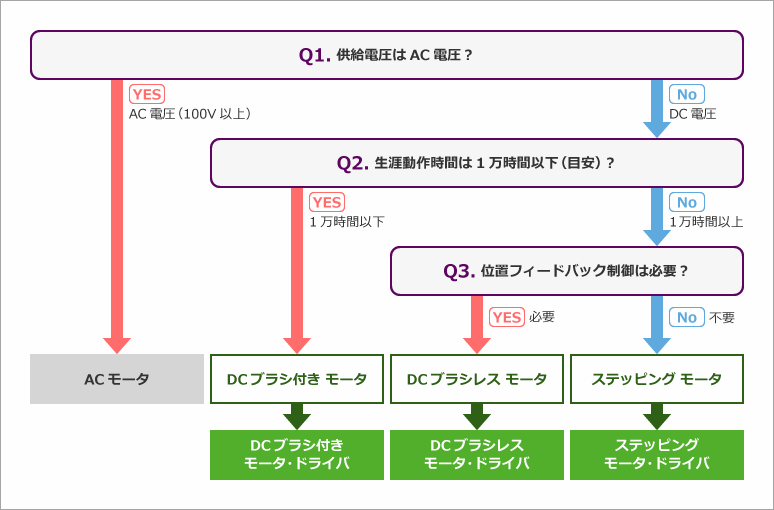
ac motor
Because of its simple structure and robustness, it is suitable for large equipment that requires durability, and is used in applications such as elevators and pumps. Since it operates at high voltage, the motor control uses a combination of isolated gate driver + high voltage FET (IGBT) or digital isolator + high voltage IPM instead of a motor driver. This time, I will introduce how to select a motor driver, so I will omit AC motors hereafter.
DC motor
Since it operates at a low voltage, it is suitable for small devices and has the advantage of low cost, making it the most widely used. However, since it includes brushes and commutator parts, there are problems with noise, uneven rotation, and mechanical deterioration. Compared to brushed DC motors, DC brushless motors are more complicated to start (acceleration is required), variable speed (frequency + voltage control), and forward/reverse rotation methods (control order, etc.). Structurally, it does not include brushes and commutator parts, so it has excellent service life, maintainability, and quietness.
stepper motor
Since it can be easily controlled by the pulse signal input to the motor, it is used in parts such as the head of printers and the part that adjusts the wind direction of air conditioners. In addition, it does not require a feedback circuit for position information, etc., and the design is relatively simple. On the other hand, it also has the disadvantage of generating heat easily because it is energized when the motor is stopped.
Up to this point, the type of motor has been determined, and the type of motor/driver has been automatically determined.
Determination of detailed motor/driver specifications
What specifications should be considered when actually selecting a motor driver? For example, there are a wide variety of items, such as basic specifications for voltage/current and protection functions, so check the table below for each type of motor.
| Operating voltage range | ______ [V] to ______ [V] |
| output current | Peak ______ [A], Average ______ [A] |
| FETs | internal or external |
| Internal FET ON resistance value | ______ [mΩ] *Only for built-in FET |
| PWM frequency | ______ [Hz] *Only when using PWM IF |
| protective function | Overcurrent protection function (OCP) / thermal shutdown function (TSD) / undervoltage lock function (UVLO) |
| package | Type/Size/Number of Pins |
| with DC brush motor driver |
DC brushless motor driver |
stepping Motor driver DC |
| Connection interface with microcomputer PWM / PH・EN / I2C |
Connection interface with microcomputer PWM/SPI/Analog |
Connection interface with microcomputer PWM / PH・EN / SPI / INDEXER |
| Number of H-bridges ______ [Pieces] |
Hall sensor feedback terminal Yes or No |
Number of steps (Full to 1/256) _______ [Step] |
| - | Current sense amplifier internal or external |
Motor type bipolar or unipolar |
| - | Conduction angle control Yes or No |
- |
The above items are divided into "common items" and "motor-specific items". "Items by motor" describes the specific conditions for each motor and driver. By selecting all items without omission, you can select the optimum motor/driver for your development application and specifications.
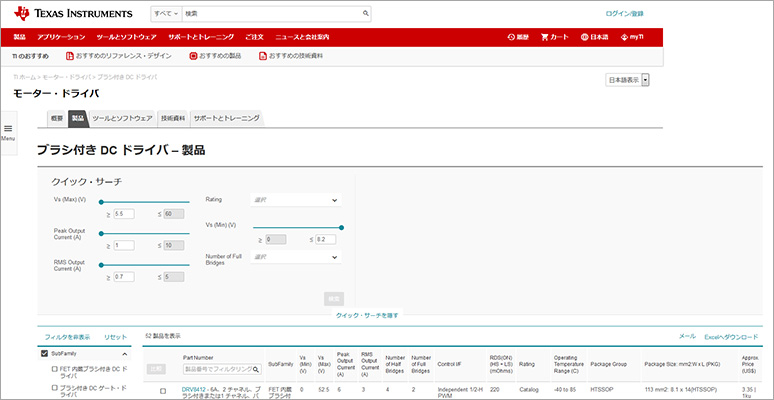
In addition, on the TI website, there is a function to view the above specifications of each motor/driver product in a list and instantly select the corresponding device. Please take advantage of this as well.
List of DC Brushed Motor Drivers
DC brushless motor/driver list
List of stepping motor drivers
Five Recommended Motor Driver Evaluation Boards from TI
From here, we will introduce recommended evaluation boards for motor drivers. It is listed for each type of motor and driver, and has a catchphrase that makes it easy to understand the features of the product at a glance, so please take a look at what you are interested in.
DC brushed motor driver
1. DRV8870EVM: Compact, High Efficiency, Wide Input Voltage Range DC Brushed Motor Driver

- Wide input voltage range: 6.5 to 45[V]
- Small package: SOP-8 4.9[mm] x 6.0[mm]
- Large current: 3.6[A] (peak value, built-in FET)
- Supports protection functions: OCP, TSD, UVLO
- Application examples: Printers, toilet shut-off valves, and other industrial equipment
Reference article
Motor driver evaluation module "DRV8870EVM" for immediate evaluation of brushed DC motors
2. DRV8837EVM: Ultra-compact, high-efficiency, dual-supply DC brushed motor driver
- Battery-operable low voltage range: Vcc=1.8 to 7 [V], VM=0 to 11 [V]
- Ultra-compact PKG: WSON-8 2.0 [mm] x 2.0 [mm]
- High Efficiency: 100nA Supply Current in Sleep Mode
- Large current: 1.6 [A] (peak value, built-in FET)
- Supports protection functions: OCP, TSD, UVLO
- Application examples: cameras, DSLR lenses, toys
DC brushless motor driver

- Wide input voltage range: 6 to 60[V]
- 100% duty: Built-in self-excited charge pump
- Protection functions: OCP, TSD, UVLO, charge pump voltage monitoring function (CPUV), each gate driver failure detection (GDF)
- Built-in power supply that can output 0.8 to 60V/600mA: Built-in DCDC for each control
- Built-in current sense amplifier
- Application examples: fan/pump motors, cordless vacuum cleaners, robots
* MSP-EXP430F5529LP is required separately for development/evaluation of this product. Click here to purchase.
Stepping motor driver
4. DRV8711EVM: 1/256 microstep compatible stepping motor pre-driver with wide input voltage range
- Wide input voltage range: 8 to 55 [V]
- Microstep: Can be set from Fullstep to 1/256step
- Protection function support: In addition to OCP, TSD, UVLO, step-out detection function (STALL)
- Easy control by microcomputer: Operation possible with INDEXER, switching with PWM is also possible. Simple current control with AutoTune, Decay control
- Built-in 5V/10mA power supply: Built-in LDO with 5V power supply for control
- Application examples: conveyors, printers, robots
5. DRV8884EVM: 1/16 microstep compatible stepping motor driver with built-in current sense

- Wide input voltage range: 8 to 37 [V]
- Microstep: Can be set from Fullstep to 1/16step
- Large current: 1.0 [A] (peak value, built-in FET)
- Protection function support: In addition to OCP, TSD, UVLO, charge pump voltage monitoring function (CPUV)
- Small PKG: HTSSOP (24) 7.8 [mm] x 4.4 [mm], built-in current sense resistor
- Easy control by microcomputer: Operation possible with INDEXER, switching with PWM is also possible
- Application examples: scanners, printers, security cameras
Start your design now with the right motor driver
What did you think. When developing applications that use motors in the future, we hope that the contents of this article will be useful in selecting the optimal motor driver.
Also, if you are considering purchasing a recommended evaluation board, the user guide for the board is available on the TI website. Why don't you refer to them and evaluate them on the board?
Contact Us
If you would like more information about the TI motor driver products introduced in this article, please contact us here.
Related information
Click here for recommended articles/materials
Motor driver evaluation module "DRV8870EVM" for immediate evaluation of brushed DC motors
Three Perspectives to Consider in Motor Control
LAUNCHXL-F28027F realizes sensorless motor control in just 5 minutes
Motor control using a microcomputer -Brushless DC motor control explained with video-
I tried to operate a brushless DC motor and encoder with Sitara AM437x
Click here to purchase products
DRV8870EVM
DRV8837EVM
MSP-EXP430F5529LP
BOOSTXL-DRV8323RH
DRV8711EVM
DRV8884EVM
Click here for manufacturer site/other related links
Evaluation Module “DRV8870EVM” User Guide
Evaluation Module “DRV8837EVM” User Guide
Evaluation Module "BOOSTXL-DRV8323RH" User Guide
Evaluation Module DRV8711EVM User Guide
Evaluation Module DRV8884EVM User Guide

