Introduction
Hello, I'm Dophie.
The second half has finally started.
The training has been completed, and the actual work as an FAE is starting little by little.
Well, this time I will talk about linear regulators and switching regulators, which I briefly touched on in the previous article.
DC-DC converters are broadly divided into these two types.
Comparing Linear Regulators and Switching Regulators
Did you get an overview of each in the previous article?
This time, we will consider the merits and demerits of each while comparing the two regulators.
Table 1 compares linear regulators and switching regulators.
The comparison items are the basic specifications that should be considered when using a DC-DC converter.
|
|
linear regulator |
switching regulator |
|
voltage conversion |
Buck only |
Buck, Boost, Inverting, Buck-Boost |
|
efficiency |
Output power/input power (often low) |
~ around 95% (generally high) |
|
output power |
Low power (typically a few watts) |
Large power possible |
|
fever |
Big |
small |
|
noise |
small |
Large switching noise |
|
design |
Simple |
複雑 |
|
Number of external components |
few |
many |
|
cost |
inexpensive |
expensive |
Table 1: Comparison of Linear and Switching Regulators
I explained about voltage conversion and efficiency in the previous article.
Associated with it is fever.
Losses in DC-DC converters are basically released as heat. Therefore, a linear regulator with lower efficiency will generate significantly more heat.
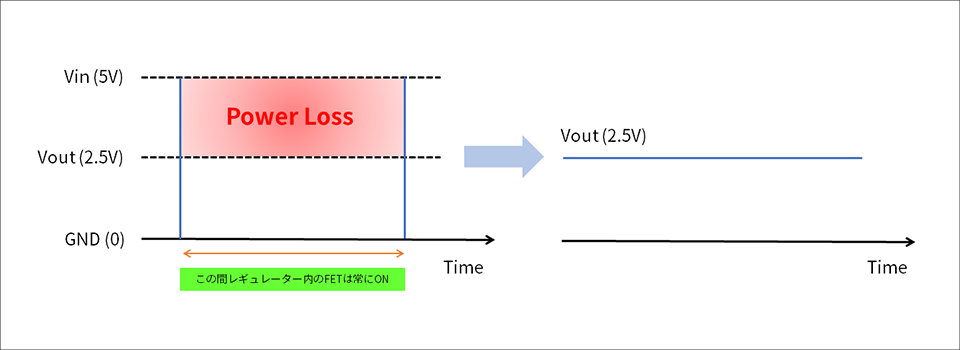
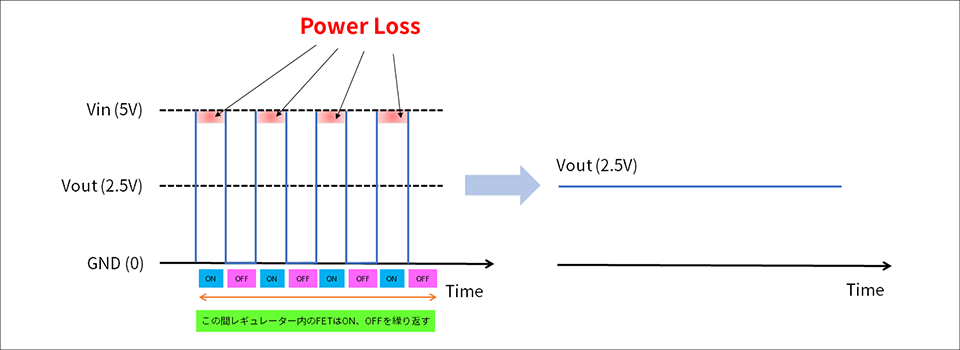
Power Loss = calorific value. Fig. 1 shows the linear regulator and Fig. 2 shows the transformation method of the switching regulator.
*In addition, Vin and Vout in Fig. 1 and Fig. 2 are assumed to be the same value.
設計、外付け部品数に関して
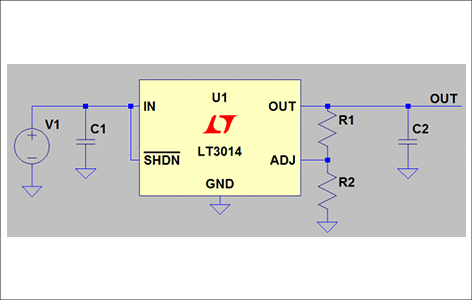
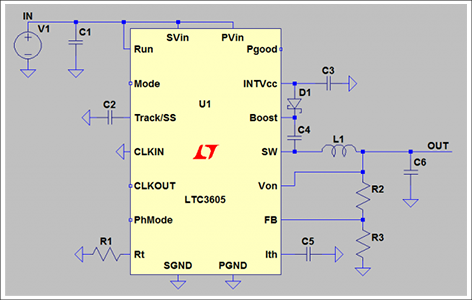
Figure 3 shows a circuit example of a linear regulator, and Figure 4 shows a circuit example of a switching regulator.
The yellow part is the IC, and the others are external parts.
《Explanation》
As you can see, the linear regulator has a very small number of external parts and a simple circuit configuration.
On the other hand, switching regulators have a large number of parts, and you can see that the circuit configuration is complicated.
Applications of linear regulators and switching regulators
As shown in the previous section, both have advantages and disadvantages.
Also, which one to use depends on the intended use.
Table 2 shows specific uses for each.
|
type |
linear regulator |
switching regulator |
|
Usage |
・For analog circuits ・Low power, low cost applications |
・For high-power logic circuits ・Applications that require low power consumption ・Applications that emphasize efficiency |
Table 2 Usage of each regulator
In this way, both have their uses, so it cannot be said unconditionally which one is better, but in recent years, most DC-DC converters have become switching regulators.
at the end
This time we talked about linear regulators and switching regulators.
Are you getting more and more understanding of "power supply"?
Analog is deep, so I still have a lot to study. . .
Let's do our best together!
Thank you for your next article!
Finally, we would like to introduce the analog IC manufacturers that we deal with.
Analog Devices
A leading manufacturer of high-performance standard analog ICs.
We determine the performance and quality of our customers' final products, such as amplifiers, battery management, data converters, high frequencies, interfaces, voltage regulators, and voltage references, and achieve stable supply.
In principle, we will not discontinue the production of our products, so customers who use our products for a long period of time, such as industrial equipment, can use them with peace of mind.


