DDSって、なに?
DDS is a circuit that generates a signal waveform at any frequency from a reference clock. It may be easier to understand if we explain it as a technology that is also used in function generators.
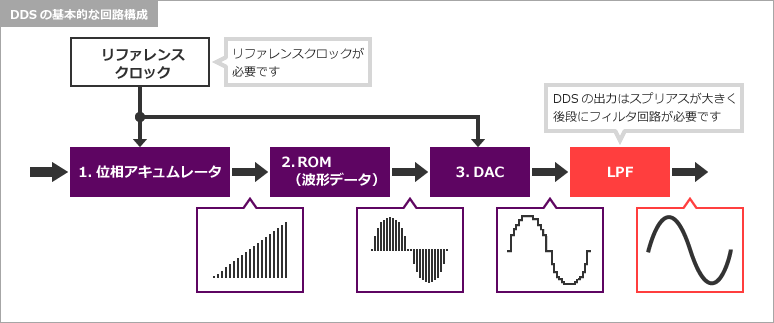
I will not explain the operation of DDS, but as a circuit,
- phase accumulator
- 波形データが書き込まれたROM
- アナログ信号に変換するDAC
It is made up of.
DDS has high frequency resolution, easy sine wave output, and the ability to switch frequencies instantly. On the other hand, spurious signals are generated, so a filter circuit is required at the subsequent stage. Also, DDS cannot generate frequencies higher than the reference clock. Therefore, if you want to generate a higher frequency than the reference clock, you need to combine a PLL in the latter stage.
Although it is possible to implement a DDS circuit using FPGA, etc., there are also products whose functions are consolidated into a single chip.
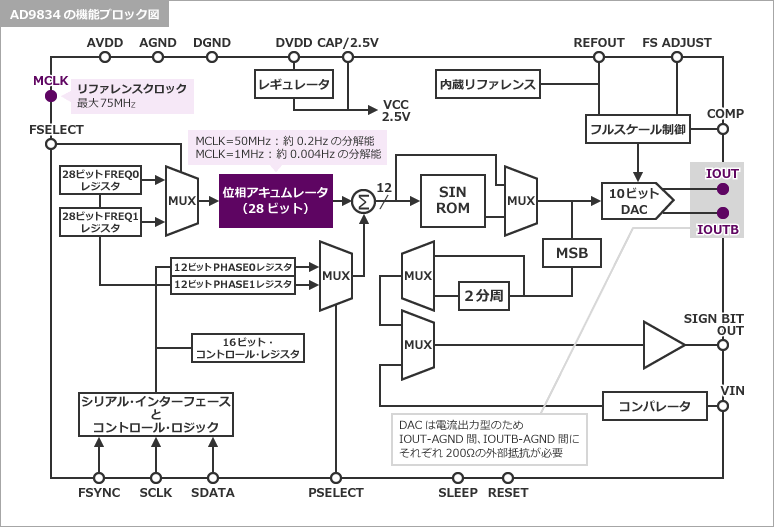
シンプルな構成のAD9834
In order to help you better understand DDS, I will use Analog Devices' AD9834, which has relatively simple functions, to explain it.
The AD9834 can generate sine/triangle waves with an output frequency of less than 37.5MHz at a reference clock of 75MHz. Typical applications include waveform generation, frequency phase tuning/modulation, low power RF/communication systems, liquid and gas flow measurement, sensor applications such as proximity, motion, and defect detection, test equipment, medical equipment, and a variety of other applications. It can be used for any purpose.
The configuration is shown below.
特長は?
The main features of the AD9834 are shown below.
High frequency resolution (frequency can be changed in steps of several Hz)
The frequency resolution is greatly influenced by the resolution of the phase accumulator, and since the AD9834 has a 28-bit phase accumulator, the frequency resolution is MCLK/2^28.
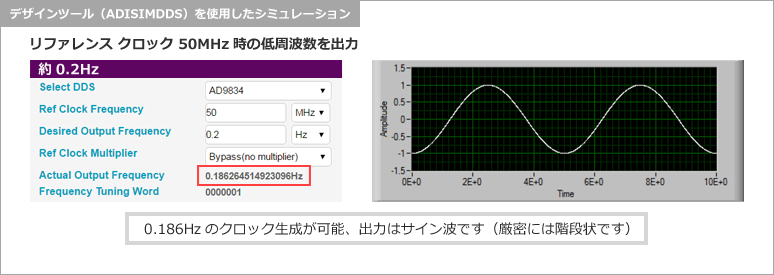
For example, when MCLK=50MHz, 50MHz/2^28=0.1862...Hz, approximately 0.2Hz resolution.
Capable of generating low frequencies
DDS can generate waveforms with frequencies below the reference clock (actually below the Nyquist frequency). Unlike the PLL method, this circuit is suitable for low frequency generation.
Frequency switching can be done instantly
The AD9834 has two frequency registers and two phase registers, which can be switched by pin setting. By using this function, FSK and PSK modulation is easy.
Sine wave output possible
Since sine wave data is written in the waveform data ROM, a sine wave can be output. In addition to sine waves, the AD9834 can also output triangle and square waves (using an internal comparator).
ここでちょっと実験
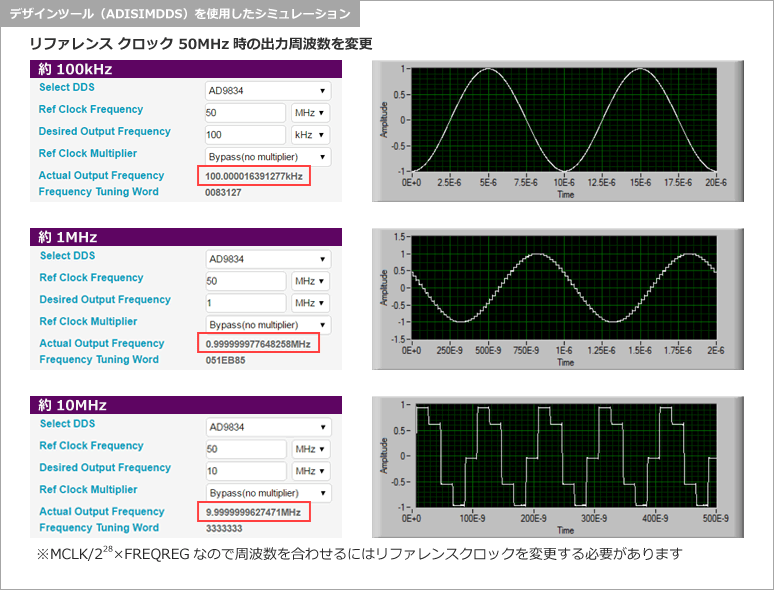
Since DDS can generate low frequencies, we will use Analog Devices' web version design tool (ADISIMDS) to check the output frequency and waveform by simulation.
By the way, if you set the frequency to 100kHz, 1MHz, or 10MHz, the output waveform will gradually become rougher.
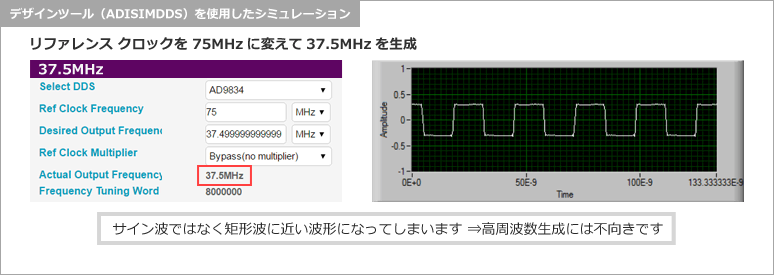
試しに、高周波数設定最大の37.5MHzを設定してみました。サイン波というより、ほぼ矩形波です。
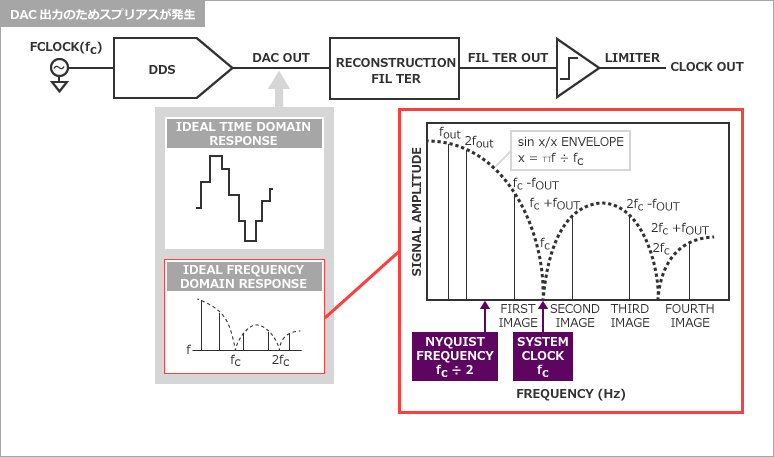
DAC出力のためスプリアスが発生してしまう
Next, I would like to explain that DDS, which I explained at the beginning, generates spurious signals.
As shown in the simulation results above, the DDS output outputs a step-like waveform. This is unavoidable since the output is passed through the DAC, but as a result spurious signals will occur.
どんなスプリアスが発生するか、ADISIMDDSを使用すればシミュレーションできますので、念のため確認してみます。
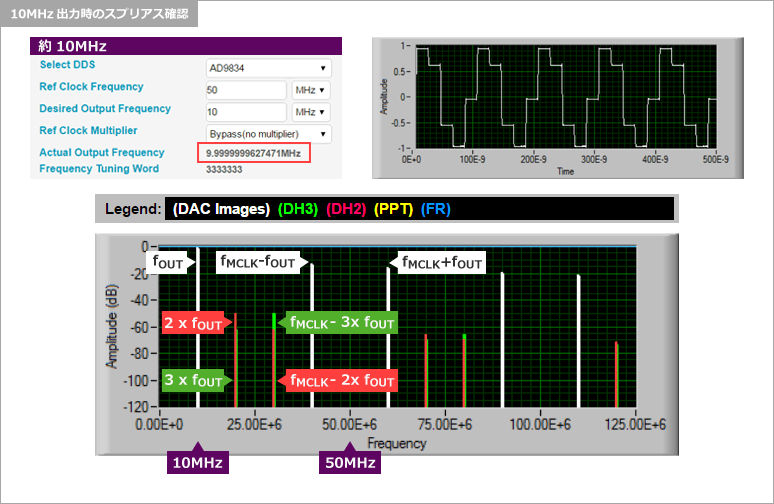
Since spurious signals are generated, a filter circuit to remove spurious signals is required after the DDS.
Next time, I will explain how to use a spurious removal filter.
Inquiry
If you have any questions regarding this article, please contact us below.
Analog Devices Manufacturer Information Top
If you want to return to Analog Devices Manufacturer Information Top, please click the button below.