This column will explain the interface that connects the Ethernet MAC and Ethernet PHY.
MII (Media Independent Interface) in Ethernet
Ethernet hardware configuration
The physical layer of Ethernet is specified in various ways, such as coaxial cable, twisted pair cable, and optical fiber cable, depending on the transmission distance and communication speed. In order to efficiently connect these differences in physical connection specifications, it is divided into a physical layer (Layer 1 (PHY)) and a logical layer (Layer 2 (MAC)). The standard interface defined for the purpose of connecting this physical layer (Layer 1) and logical layer (Layer 2) is the MII.

MII (Media Independent Interface) is equivalent to the AUI of the 10BASE standard and was defined in the ``IEEE 802.3u'' of 100 Mbps Ethernet, but MII corresponding to 10 Mbps and 100 Mbps, GMII corresponding to 1000 Mbps (1 Gbps), 10 Gbps There is XGMII that supports .
Next, I will briefly explain MII, RMII, GMII, and RGMII.
MII (Media Independent Interface)
MII (Media Independent Interface) has a clock and 4-bit wide data bus for transmission and reception respectively. Generated by PHY.
Achieves 25MHz (clock frequency) x 4bit (data path) = 100Mbps.
(2.5MHz (clock frequency) x 4bit (data path) = 10Mbps)
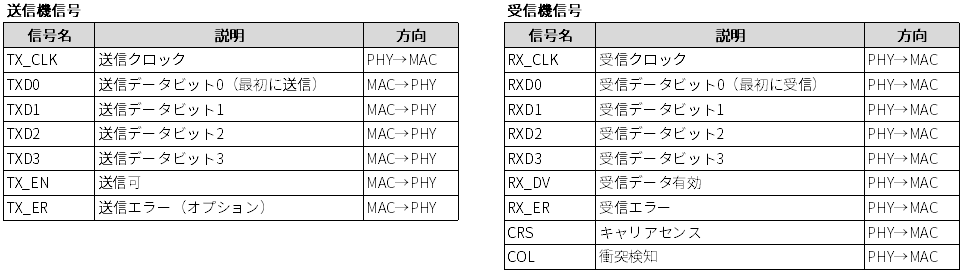
Source: Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
RMII (Reduced Media-Independent Interface)
RMII (Reduced Media-Independent Interface) is a standard developed to reduce the number of signals connecting PHY and MAC. It achieves 100Mbps communication with a 50MHz clock (100Mbps/10Mbps both operate at 50MHz) and a 2-bit wide data bus.
Achieves 50MHz (clock frequency) x 2bit (data path) = 100Mbps.
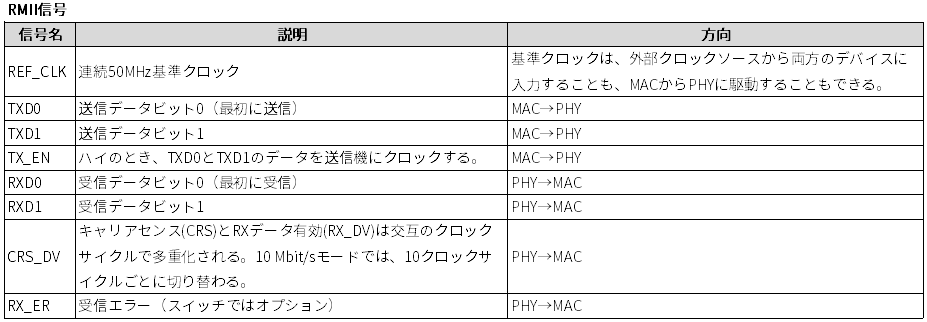
Source: Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
GMII (Gigabit Media-Independent Interface)
GMII (Gigabit Media-Independent Interface) has a 125MHz clock and an 8-bit wide data bus for transmission and reception, realizing a maximum communication speed of 1000 Mbps.
Achieves 125MHz (clock frequency) x 8bit (data path) = 1000Mbps.
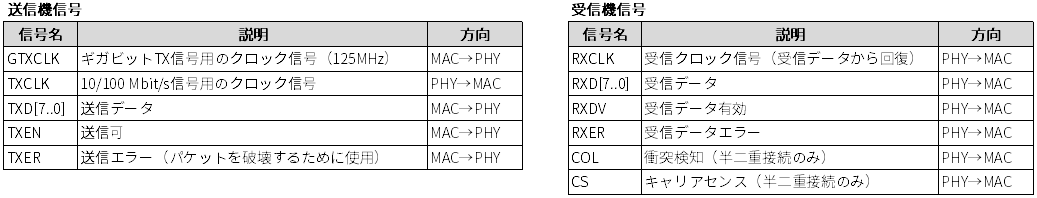
Source: Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
RGMII (Reduced Gigabit Media-Independent Interface)
RGMII (Reduced Gigabit Media-Independent Interface) cuts the data bus of GMII in half. At 1000Mbps data is sent on both the rising and falling edges of the clock. At 10/100Mbps, data is only sent on the rising edge of the clock.
Achieves 125MHz (clock frequency) x 4bit (data path) x 2 = 1000Mbps.

Source: Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
SGMII(Serial Gigabit Media-Independent Interface)
SGMII (Serial Gigabit Media-Independent Interface) defined by Cisco Systems is a standard for serial transfer of 1000Mbps with 8B/10B encoding. A DDR differential pair with a clock frequency of 625MHz is used for TX/RX Data and TX/RX Clock, but the TX Clock is optional and is not normally used. Instead, the RX Clock is recovered from the data of the differential pair by CDR (Clock and Data Recovery). Data is encoded using 8B/10B Code-Groups. (See IEEE802.3 std. Chapter 36 for information on 8B/10B Code-Groups.)
Typically used for Gigabit Ethernet, but also applicable to 10/100 Mbit/s Ethernet.
Achieves 625MHz (clock frequency) x 1bit (data path (serial transfer)) x 2(DDR) = 1250Mbps.

Microchip Ethernet related product information
Click below for information on Microchip's Ethernet related products.
Inquiry
If you have any questions regarding this article, please contact us below.
To Microchip manufacturer information Top
If you want to return to Microchip manufacturer information top page, please click below.
