
Surprisingly, China is actively working on the SDGs. In the background is the reality of facing worsening social problems such as environmental destruction and economic disparity. Therefore, we will introduce how China is using its own technology, which has made remarkable progress in the past few years, to tackle the problems of the SDGs. We hope that the information on the utilization of digital technology will be used as a hint for building a business model, and also for how to make use of it for business in China.
■ Why China's SDGs - Why China attaches great importance to SDGs
First, let's briefly review the SDGs. SDGs is an abbreviation of "Sustainable Development Goals", which means sustainable development goals and consists of 17 international goals with a deadline of 2030. It was unanimously adopted at the United Nations Summit in September 2015.

Source: International Cooperation Bureau, Ministry of Foreign Affairs
According to the non-profit Sustainable Development Solutions Network (SDSN), China ranks 39th out of 162 countries in terms of achievement of the SDGs. Japan is ranked 15th, so even if you compare it with that, it can be said that there is still a long way to go.
However, in China, industry, government, and academia are working together to promote initiatives for the SDGs. The government has incorporated the content of the SDGs into each item of the 14th Five-Year Plan and is formulating country-specific plans for implementing the 2030 SDGs agenda. On the academia side, Tsinghua University has signed a memorandum of understanding with the University of Geneva in Switzerland to establish the world's first "Global SDGs Research Institute" at the School of Public Management. In the industrial world, major companies are disclosing sustainability reports and actively making investments and donations for the SDGs.
In this way, China is extremely proactive in its efforts to achieve the SDGs, but the reasons for this include "large social disparities" and "serious environmental problems."
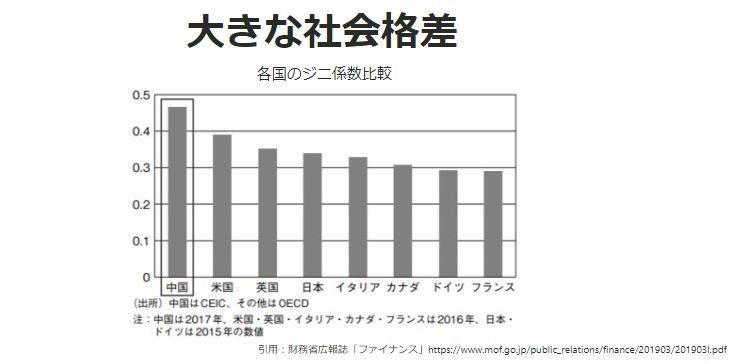
Quote: Ministry of Finance public relations magazine "Finance"
The Gini coefficient is a measure of income inequality. Comparing each major country with this, you can see that the income disparity in China is overwhelmingly large. The closer the index is to 1, the greater the income disparity is, and if it exceeds 0.4, it is said to pose a significant social problem.
Roughly expressing this disparity, there are 2,755 “billionaires” in China with assets of $1 billion or more in 2020. This is the highest number in the world. In addition, it is said that there are about 600 million people with a monthly income of 1,000 yuan (about 15,000 yen) or less in 2020. I have to say that the economic disparity is quite large.
As a "serious environmental problem", first of all, the amount of CO2 emissions is the highest in the world. The temperature rise rate of the country is also higher than the world average. There is a more serious problem of PM2.5 (air pollution), and thousands of people are said to have died due to air pollution in Beijing, Shanghai, Guangzhou, etc. A 2007 World Bank study found that air pollution kills hundreds of thousands of people every year across China. In addition to air pollution, water pollution and soil pollution also make it an urgent task to solve environmental problems.
Despite these various problems, China's progress in digital technology is astonishing, especially in the fields of AI and data science. In the 2021 edition of the CS (Computer Science) ranking AI field targeting universities around the world created by Professor Emery Berger, a computer science expert at the University of Massachusetts Amherst, Chinese universities account for four of the top five. I was. Unfortunately, Japanese universities are not even in the top 15 in this ranking.
The focus here is on how the world's leading digital technology can be used to solve the serious challenges related to the SDGs. By looking at the current and future efforts of China, Japanese companies can also gain various hints.
■ How to use digital technology for SDGs related issues
First, let's take a look at measures to address economic inequality.
In China, digital technology is being used to combat poverty in rural areas. For example, "rural live commerce". This is being worked on by major IT companies such as Alibaba and Weibo, where they introduce and sell agricultural specialties through live video on the internet. We provide an EC platform for farming villages and produce special products of each farming village.
We also use big data to support poverty. For example, Guizhou, east of Yunnan Province, known as "China's poorest province," had a rural poverty population of 8.9% nationwide and a poverty incidence rate of 18% according to a 2015 survey. There, Guizhou Province and a major Chinese IT company (Inspur) built a "poverty alleviation cloud with big data", and based on GPS location information, households using various data such as houses, agricultural production, and labor conditions. quantified the poverty of the population with high accuracy.
Until now, it was not possible to ascertain the poverty level of each household, but by using the cloud, it becomes possible to ascertain the actual situation of the households that need support, preventing fraud and providing the necessary support to the households that need it. I was able to build a mechanism to reach. We have connected more than 2 million poor households with the government and realized livelihood support.
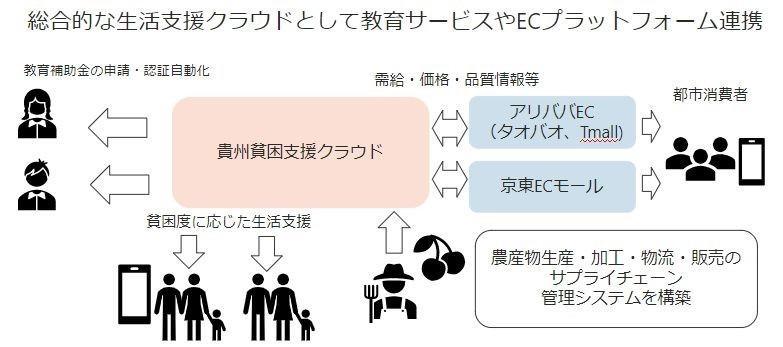
After that, in China, these efforts were linked with educational services and EC platforms as a comprehensive life support cloud. As a result, we have been able to grasp the actual situation of children in households who cannot receive education, and we are able to provide appropriate support. The connection between urban consumers and rural villages has created opportunities for increased income, and a supply chain management system for production, processing, distribution, and sales has been built, leading to more efficient business operations. .
As a result of these efforts, it is said that the number of people living in extreme poverty (annual income of 2,300 yuan or less) across China was 98.99 million in 2012, but has dropped to zero in 2020. In 2013, the average annual income in rural areas of China was 6,079 yuan (about 97,000 yen), but in 2020 it increased to 12,588 yuan (about 200,000 yen).
Of course, we can't take the figures announced in China as false, but at least we can assume that the eradication of poverty is progressing at a considerable speed. In addition, it is difficult to apply big data used in farming villages to Japan as it is because of problems such as personal information. However, by overcoming various barriers, we may be able to see a solution to the disparity between rural and urban areas.
Next, what about initiatives for decarbonization?
China has declared zero carbon emissions (carbon neutral) by 2060 and is gradually reducing the ratio of thermal power generation in its power supply mix. Furthermore, although the ratio is small, renewable energy such as nuclear power generation and wind and solar power show high growth rates. In addition, in the 14th Five-Year Plan (2021-2025), 9 major bases and 4 offshore wind farms that will be the pillars of clean energy were announced, and efforts are being made to build power grids in coastal areas where power consumption is high. doing.
In addition, major IT companies such as Alibaba and Tencent are working on energy reforms in their data centers. Alibaba has succeeded in reducing CO2 emissions by 300,000 tons in 2020 through clean energy procurement and power reduction at data centers. Furthermore, we have succeeded in improving the efficiency of steel usage and reducing paper consumption by providing industrial solutions to group companies. Tencent is procuring clean energy for its data centers in Chongqing and Tianjin, etc., and is investing approximately 800 billion yen to solve social issues.
We are also working on decarbonization with a unique app. By using the “Antforest” app for Alipay users, points are added for low-carbon actions such as using public transportation, and the virtual space tree prepared for each user grows. And by selling grown trees to non-profit organizations and environmental protection companies, it is a mechanism that leads to real tree planting. As of September 2020, over 550 million people have taken part and planted more than 223 million trees. It is said that this has contributed to the greening of deserts such as Inner Mongolia and created jobs for tree planting in the region.
What about initiatives for the environmental industry?
In China, the environmental industry (soil/air/water pollution control, environmental measurement, etc.) saw a 29-fold increase in sales from 2004 to 2019. During this period, the average annual growth rate has reached a high level of 25.5%. As for air pollution, an air quality monitoring system with fixed sensors has been built nationwide, and in some areas, efforts are being made to map the pollution situation of the entire city in real time using mobile devices attached to taxis. It seems that this mechanism has been able to detect 10 times more pollution sources than before.
The automobile industry has declared that it will promote the use of EVs, eliminate all gasoline-powered vehicles by 2035, and make all new vehicles eco-friendly. Many related startups have also appeared, and innovation is progressing throughout the automobile industry.
Environment-related startups are appearing one after another, and "Gaiya Technology", a comprehensive solution company for improving the soil environment, has developed its own equipment for soil measurement and improvement, and in 2018 it was listed as one of the top 20 next-generation unicorns in the environmental field in China. ” has been selected. In addition, alternative meats derived from plants and insects, which have a lower environmental impact, are attracting attention in China, especially among the younger generation. In China, start-up companies such as “Starfield”, “Hey meat”, and “Youkuai” have appeared and are beginning to take proactive measures.
■Summary of China's SDGs and Issues-China's SDGs Issues and Japan's Efforts
Although China is certainly lower than Japan in the SDGs achievement status ranking, you can see that it has introduced initiatives that Japan has not been able to implement, and is moving forward dynamically and steadily.
According to SDSN's evaluation, China currently has achieved the goals of "education" and "growth and employment" among the 17 goals. On the other hand, “social inequality” and “climate change” are still considered “main goals”.
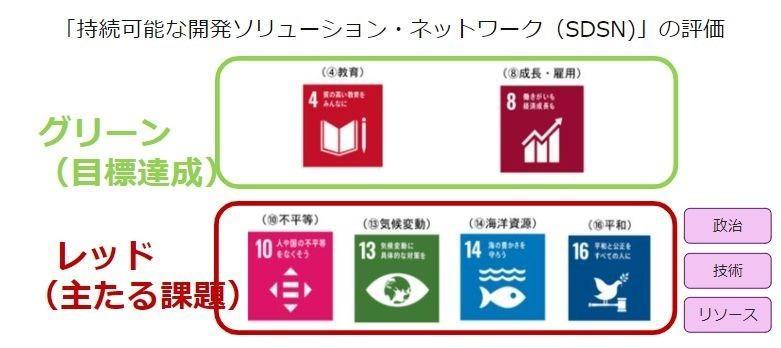
I believe that some of these main goals will be difficult to achieve due to the influence of China's political system, but there are also cases where it is not possible to achieve them due to a lack of technical resources. There should be.
In China, the government is actively using digital technology for air monitoring and other measures that require massive data processing, as well as models that skillfully combine business and social issues, such as e-commerce and mobile payment tree planting. increase. However, although the environmental industry has become a growth industry, it is only halfway as a countermeasure for the SDGs. Under such circumstances, it is believed that there are still opportunities for companies with high-level environmental technology and excellent environment-related business models to enter the market.