【加速度センサー入門】シリーズでは、アナログ・デバイセズ社の加速度センサーを中心に、基本的な使い方や応用方法を解説します。
本記事では、前回に引き続きArduionoとADXL345を使って角度(傾斜角)計測をおこなっていきます。前回角度測定をした際、水平に置いた場合の理想の角度は0°ですが、実際は数°の誤差を含んでいました。今回はこの誤差を取り除いていきたいと思います。
【加速度センサー入門】シリーズ一覧はこちらから
角度計測におけるオフセット誤差の影響を考えてみる
前回の記事(【加速度センサー入門】第13回 :加速度センサーで角度を測ってみよう(その1))では角度検出の原理について説明せていただきましたが、あくまでも理想状態での話となります。一般的にMEMS構造は機械部分を持っているデバイスであるため、システムの組立て時に PCB などから加わる応力によりオフセットと感度が影響を受けることがあります。
今回は角度ということで改めてオフセット誤差の影響を考えていきます。ADXL345のオフセット誤差はTypで35mgとなっています。1°あたりの加速度変化は17.4mgとすると約2℃の誤差をもっていることになります。この誤差を取り除く方法としてはキャリブレーションがあります。詳細は以前ご紹介させ頂きました「【加速度センサー入門】第12回 :オフセットキャリブレーションをおこなってみよう」の記事で説明をしていますのでご参照ください。また下記のアプリケーションノートでも詳しく解説していますので合わせてご参照ください。
AN-1057: 加速度センサーによる傾きの検出加速度センサーによる傾斜測定の精度を高める
Arduinoを使って試してみよう
加速度センサー「ADXL345」とハードウェアのオープンプラットフォームである「Arduino」を使い重力加速度の変化量を計算し、傾斜角度を求めるサンプルプログラムを作成していきます。今回は、前回の内容にオフセット誤差を取り除くキャリブレーションの処理を追加する形となります。
準備するもの
今回、加速度センサーを評価するうえで準備したものはこちらです。
・Arduino IDE がインストール済みの PC (Arduino IDE のダウンロードはこちらから)
・Arduino Nano 互換品ボード
・加速度センサー ADXL345
・その他(USB ケーブル (Arduino と PC 接続用)、ブレッドボード、ワイヤー)
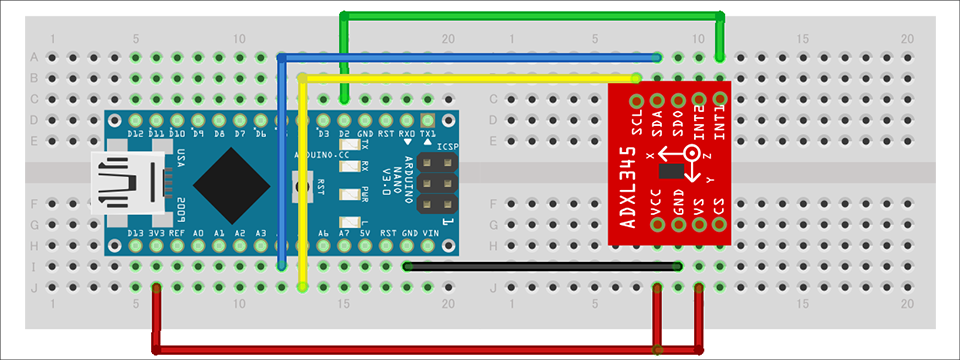
上記の部品を組み合わせて、下図のように回路を組んでいきます。Arduino Nano への電源は、PC からの USB バスパワーで供給します。ADXL345は、SPI インターフェースとI2C インターフェースに対応していますが、今回はI2C インターフェースを使用します。また割り込みピンのINT1ピンを使用します。
プログラムの内容
今回のプログラムでは起動時に一度キャリブレーション処理を実施し、オフセット誤差を取り除いた形で、角度計算をおこなっていきます。Arduino IDE で作成したプロジェクトファイルはダウンロードできますので、ご興味のある方は下記「資料ダウンロード」より入手ください。
なお、本サンプルプログラムでは#define OFFSET_CALIBRATION をコメントアウトするとキャリブレーション処理をスキップできますので、「あり・なし」の効果を確認することができます。ぜひお試しください。
動作確認
作成したプログラムの動作確認をおこないました。動画の通り水平にデバイスを置いた際のピッチ・ロール角は2度ほどの誤差をもっているのが確認できます。キャリブレーション処理を実施すると、誤差の影響は減り、0度付近に近づいたことが確認できたかと思います。
このとおり角度計測において初期のオフセット誤差を取り除くのは重要となります。角度計測についての記事はもう少し投稿していきたいと思いますので、次回の記事もお楽しみにしてください。
今回検証したサンプルコードのダウンロード
今回実施したArduino のプロジェクトファイルを提供しています。こちらからお申し込みの上、ぜひお試しください。
加速度センサー ADXL345 について
今回使用したADXL345 は、3軸のデジタル出力加速度センサーです。主な特長は下記の通りです。
・ADC、演算機能ブロック、FIFO 内蔵で、非常に使いやすいスタンダードな加速度センサー
・加速度データは、デジタルシリアル方式で一般的なI2C/SPIを採用
・3軸タイプのセンサーは直交座標 (X, Y, Z) で、それぞれの軸に働く加速度を取得可能
・最大検出加速度を2g~16gの範囲で設定ができ、サンプリングも~3.2kHzと幅が広いので、衝撃、傾き、モーション検知など様々な用途に応用可能
・消費電流を減らすためのフレキシブルなモードを採用
ADXL345 の詳細は、データシートをご参照ください。また、この加速度センサーは非常に使いやすいので、これから加速度センサーを評価してみたいという方は、ぜひ評価ボードでお試しください。
最後に
本記事の内容に関してのご質問、または加速度センサーの選定や使い方にお困りのことがありましたら、以下からお問い合わせください。
アナログ・デバイセズ メーカー情報Topへ
アナログ・デバイセズ メーカー情報Topに戻りたい方は以下をクリックしてください。
