
こんな方におすすめの記事です
データ分析関連の知識を身につけたいエンジニアの方
この記事を読み終えるのにかかる時間
5分
はじめに
製造工程からのデータ収集やデータ分析をお客様から依頼される機会がどんどん増えてきています。
製造現場からデータを収集できても、それを課題解決に役立つ分析結果が得られるようにするまでには、さまざまな道のりがあります。
今回は、振動データのダウンサンプリングに焦点をあて、データ分析の準備工程の一部をご紹介します。
データの前処理とは?
収集したデータを分析する際、データのフォーマットを揃えて分析しやすい形にデータを加工することを前処理といいます。
センシングデータ(センサーを利用して収集したデータ)の前処理では主に、「ダウンサンプリング」「データの結合分割」「正規化(ノーマライズ)」「オフセット処理」があります。
中でも、ダウンサンプリングによるデータの間引きがポイントとなります。
なぜデータ前処理が必要なのか
アナログ振動センサーが感知する振動は、時間が進むにつれ連続して変化します。これを一定の間隔でサンプリング(標本化)したものが、デジタル化された振動データとなります。
データ分析に必要な振動データを収集するためには、特徴を捉えるために必要な最高周波数の2倍以上のサンプリングレート(サンプリング周波数)でサンプリングを行う必要があります。
サンプリングレートが高いほどデータ量は大きくなり、分析に負荷がかかるため、データを間引くことで、データ量を小さくして負荷を減らすことがあります。
実際に間引いてみる
データを間引く前の処理としてLPF(Low Pass Filter:低域通過フィルタ)をかける必要があります。
なぜ、LPFを事前に行う必要があるのでしょうか?
それは、LPFをかけずに間引くとデータ分析に必要な特徴が変化してしまうからです。
では、どのように変化してしまうのか「LPFを行わない場合」と「LPFを行う場合」の間引き結果を比較検証してみましょう。
① 3種類の周波数を合成した波形を作成する
初めに、3種類の周波数を合成した波形を作成します。
通常振動データとは、(振動センサーで感知した)さまざまな周波数の振動データが重なり合ったものです。
本検証ではデータ特徴の変化をわかりやすくするため、1Hz、3Hz、14Hzの周波数のサイン波データを使って説明します(図1)。以下のデータは100 Hzのサンプリングレートで検証したものです。
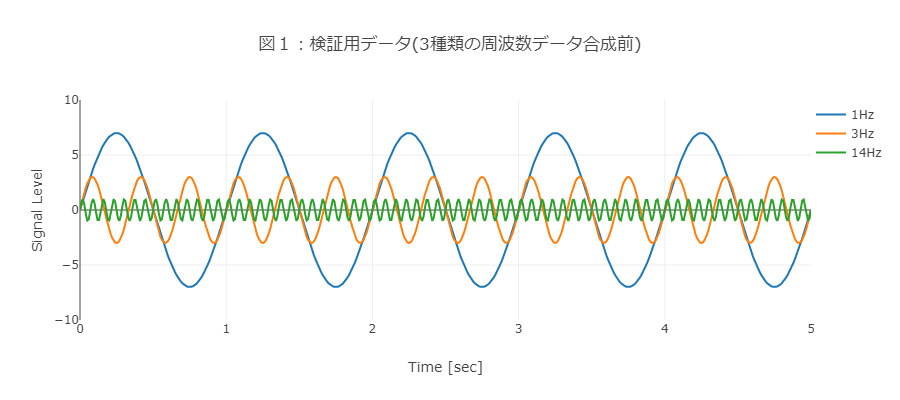
② 合成波形の周波数スペクトルを確認する
上記3つの周波数のサイン波データを合成します(図2)。
合成したデータをFFT(Fast Fourier Transform:高速フーリエ変換)にかけて周波数成分を確認すると、合成した3つのデータの周波数にピークがあることがわかります(図3)。
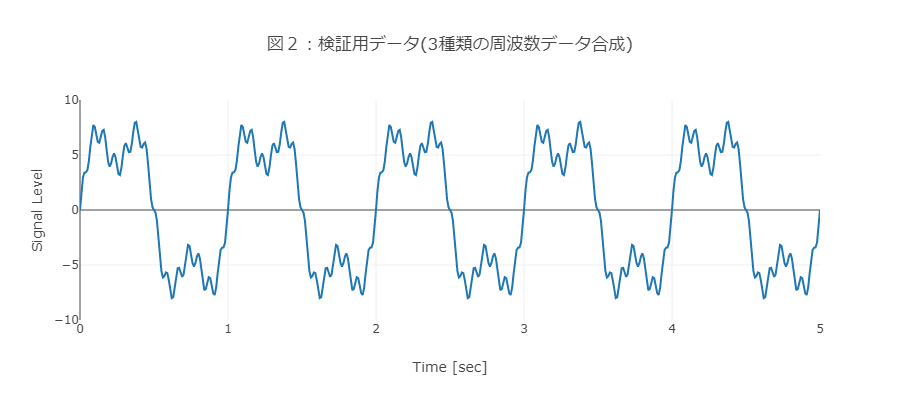
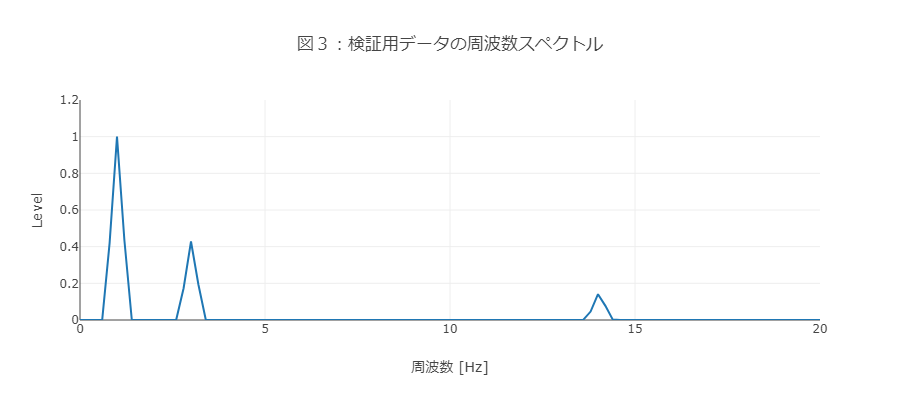
③ LPFを行わないと分析結果に悪影響を及ぼす
データを5個ごとに1つ残すように間引くことで、データ量を1/5にします(図4)。
ここでは、100Hzのサンプリングレートを1/5に間引いたため、20Hzのサンプリングレートのデータに相当します。
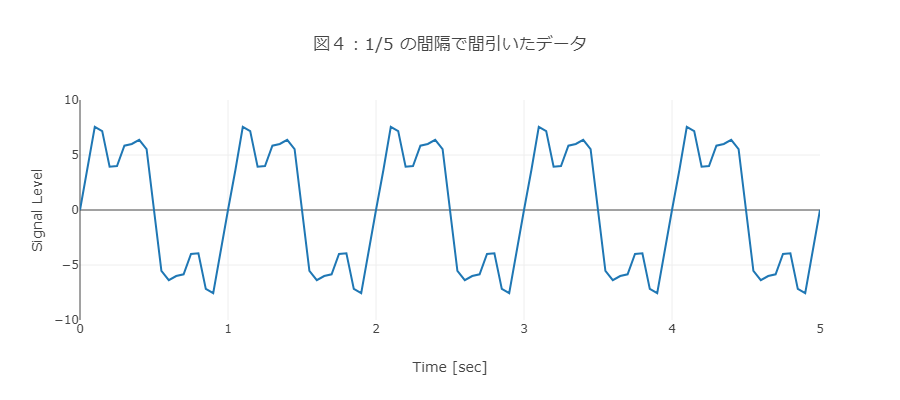
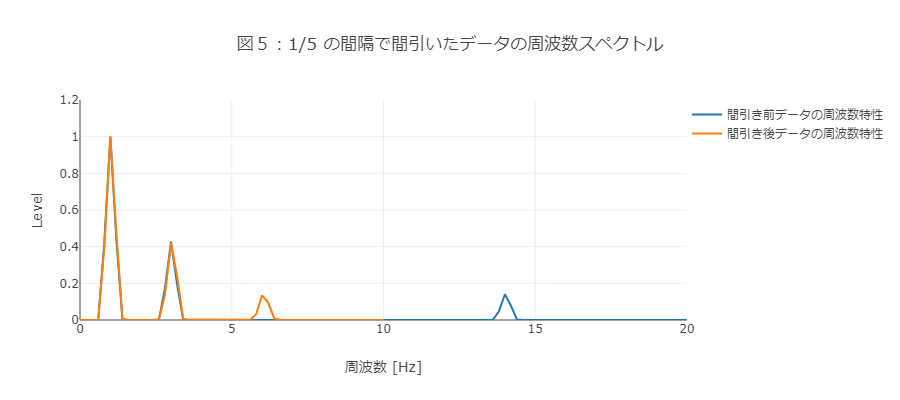
図5の合成したデータの周波数のピークに注目してみましょう。
周波数スペクトルを確認すると、間引き後は20Hzのサンプリングレートでは表現できない14Hzに相当する成分が、6Hz付近で確認できます。
これを、エイリアシング(折り返し雑音)といいます。
6Hzの振動という、本来では存在しないはずの周波数特性が表れているため、分析結果に影響が出てしまいます。
④ アンチエイリアシングを使ったダウンサンプリング
エイリアシングを防止するためのLPFのことを、アンチエイリアシングフィルタといいます。
アンチエイリアシングフィルタを使って間引きを行った場合はどのような結果になるでしょうか。
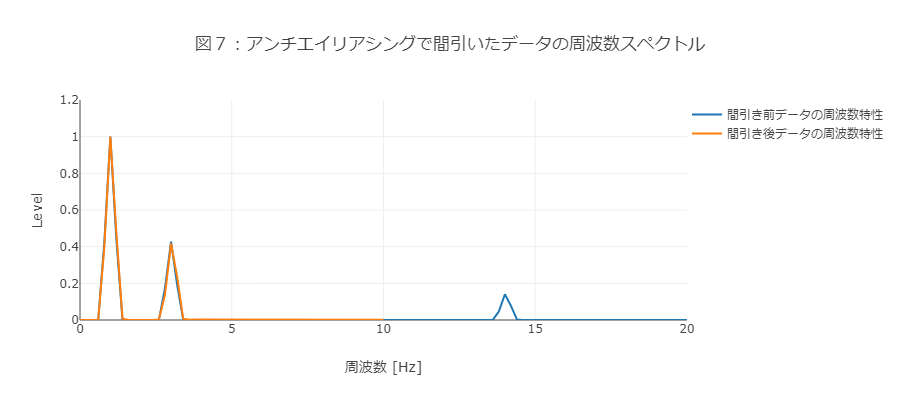
図7で周波数スペクトルを確認すると、オレンジ色で表している間引き後のデータの周波数上限は10Hzとなり、14Hzのピーク部分は表れません。
先ほど、単純にデータ量を1/5に間引いた際(図5)見えていた、6Hzでの折り返しも発生していません。
アンチエイリアシングを行うことで、エイリアシングによるデータ特性の変化を発生することなく、ダウンサンプリングが可能になりました。
まとめ
今回はデータ前処理のポイントについて、振動データのダウンサンプリングに着目してご紹介しました。
ポイント
・ 振動データを収集するためには、必要な最高周波数の2倍以上のサンプリングレートでサンプリングを行う
・ データを間引く前の処理として必ずLPFをかける
・ LPFを行わないとエイリアシングが発生し、分析結果に悪影響を及ぼす
・ アンチエイリアシングを行うことで、エイリアシングによる影響を受けることなくダウンサンプリングが可能となる
マクニカのARIH(AI Research & InnovationHub)では、最先端のAI研究・調査・実装による評価をした上で最もふさわしいAI技術を組み合わせた知見を提供し、企業課題に対する最適解に導く活動をしています。
詳細は下記よりご覧ください。